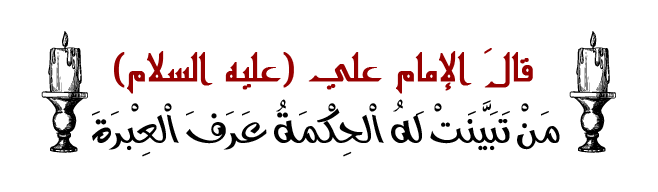
آخر المواضيع المضافة
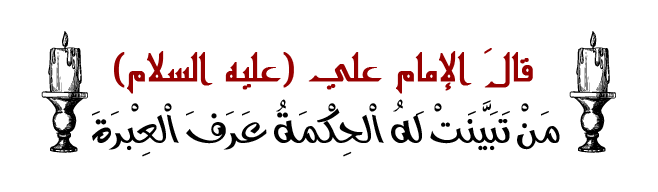

|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 18-7-2017
التاريخ: 22-3-2022
التاريخ: 21-8-2020
التاريخ: 9-8-2020
التاريخ: 25-2-2016
|













