


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 9-8-2016
Date: 1-8-2016
Date: 25-7-2016
|
Charge in Uniform Electric Field
Find the trajectory of a particle of mass m, charge e, in a uniform electric field E, assuming zero velocity parallel to E at t = 0. Sketch the trajectory in the plane of motion.
SOLUTION
The plane of motion of a particle will be defined by its initial velocity v and the direction of the electric field E. Let the initial velocity coincide with the x axis and E with the y axis. We may write the equations of motion for a charge in an electric field
 (1)
(1)
where p is the momentum of the particle. Obviously, since there is no force in the direction perpendicular to the x - y plane, the particle will move in this plane at all later times. We can write (1) in the form
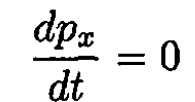 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
Integrating (2) and (3) yields
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
The energy ε of the particle (without the potential energy due to the field) is given by
 (6)
(6)
where  is the initial energy of the particle. The work done by the electric field changes the energy of the particle
is the initial energy of the particle. The work done by the electric field changes the energy of the particle
 (7)
(7)
or
 (8)
(8)
Equations (6) and (8) result in
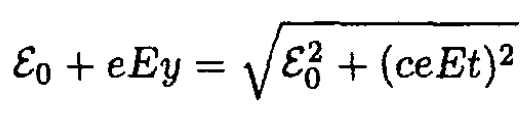 (9)
(9)
which yields
 (10)
(10)
and
 (11)
(11)
On the other hand
 (12)
(12)
Substituting px = py and py = eEt into (12) and using t from (11), we find
 (13)
(13)
Integrating (13), we obtain

For the initial conditions x0 = y0 = 0
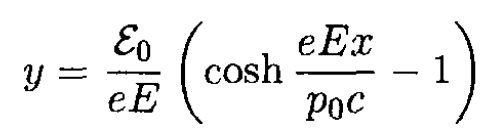 (14)
(14)
So the particle in a constant electric field moves along a catenary (see Figure 1.1, where we took e > 0). If the velocity of the particle v << c, then p0 = mv0, ε0 = mc2 and expanding cosh (eEx/p0c), we obtain

which gives the classical result for a charged particle in an electric field. Also note that (10) coincides with the result for uniformly accelerated motion in the proper reference frame, where the acceleration ω0 = eE/m and p0 = 0. Under Lorentz transformations for frames moving with velocities parallel to the electric field E, the field is unchanged.

Figure 1.1



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|