
 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 21-8-2016
Date: 4-7-2019
Date: 8-10-2020
|
Ozonolysis, or ozonolysis-reduction, refers to the treatment of an alkene with ozone followed by a suitable reducing agent to break down complex double-bond-containing compounds into smaller, more easily identified products. From the identity of the products formed, it may be possible to deduce the structure of the original double-bond-containing substance. Ozonolysis will feature prominently in many of the road-map problems that you will encounter in this course.
A molozonide is an unstable, cyclic intermediate that is initially formed when an alkene reacts with ozone.
Alkenes can also be cleaved by other oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate. However, KMnO4 will carry the oxidation further than ozonolysis, so products can be slightly different. Note within the summary of the following reactions that ozonolysis produces aldehydes and ketones, while KMnO4 can oxidize all the way to to carbon dioxide and carboxylic acid.
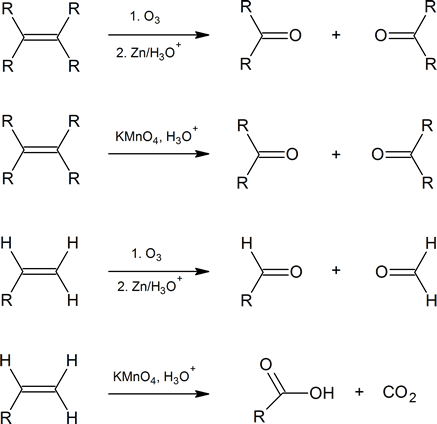
Diol cleavage is another example of a redox reaction; periodic acid, HIO4, is reduced to iodic acid, HIO3.
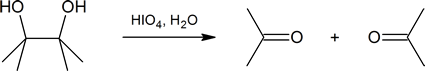
Ozonolysis is a method of oxidatively cleaving alkenes or alkynes using ozone (O3), a reactive allotrope of oxygen. The process allows for carbon-carbon double or triple bonds to be replaced by double bonds with oxygen. This reaction is often used to identify the structure of unknown alkenes. by breaking them down into smaller, more easily identifiable pieces. Ozonolysis also occurs naturally and would break down repeated units used in rubber and other polymers. On an industrial scale, azelaic acid and pelargonic acids are produced from ozonolysis.
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=476&height=116)
The gaseous ozone is first passed through the desired alkene solution in either methanol or dichloromethane. The first intermediate product is an ozonide molecule which is then further reduced to carbonyl products. This results in the breaking of the Carbon-Carbon double bond and is replaced by a Carbon-Oxygen double bond instead.
Step 1:
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=462&height=145)
The first step in the mechanism of ozonolysis is the initial electrophilic addition of ozone to the Carbon-Carbon double bond, which then form the molozonide intermediate. Due to the unstable molozonide molecule, it continues further with the reaction and breaks apart to form a carbonyl and a carbonyl oxide molecule.
Step 2:
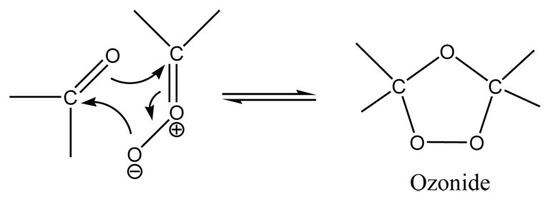
The carbonyl and the carbonyl oxide rearranges itself and reforms to create the stable ozonide intermediate. A reductive workup could then be performed to convert convert the ozonide molecule into the desired carbonyl products.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ووفد من جامعة البصرة يبحثان سبل تعزيز التعاون المشترك
|
|
|