


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-12-2020
Date: 28-1-2019
Date: 6-12-2020
|
Many nuclear decay reactions produce daughter nuclei that are in a nuclear excited state, which is similar to an atom in which an electron has been excited to a higher-energy orbital to give an electronic excited state. Just as an electron in an electronic excited state emits energy in the form of a photon when it returns to the ground state, a nucleus in an excited state releases energy in the form of a photon when it returns to the ground state. These high-energy photons are γ rays. Gamma (γ) emissionA nuclear decay reaction that results when a nucleus in an excited state releases energy in the form of a high-energy photon (a γ ray) when it returns to the ground state. can occur virtually instantaneously, as it does in the alpha decay of uranium-238 to thorium-234, where the asterisk denotes an excited state:

If we disregard the decay event that created the excited nucleus, then
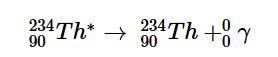
or more generally,
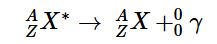
Gamma emission can also occur after a significant delay. For example, technetium-99m has a half-life of about 6 hours before emitting a γ ray to form technetium-99.
Because γ rays are energy, their emission does not affect either the mass number or the atomic number of the daughter nuclide. Gamma-ray emission is therefore the only kind of radiation that does not necessarily involve the conversion of one element to another, although it is almost always observed in conjunction with some other nuclear decay reaction.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|