


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 5-12-2019
Date: 5-12-2019
Date: 20-7-2018
|
Anomeric Forms of Glucose
Fischer's brilliant elucidation of the configuration of glucose did not remove all uncertainty concerning its structure. Two different crystalline forms of glucose were reported in 1895. Each of these gave all the characteristic reactions of glucose, and when dissolved in water equilibrated to the same mixture. This equilibration takes place over a period of many minutes, and the change in optical activity that occurs is called mutarotation. These facts are summarized in the diagram below.
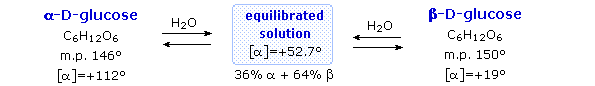
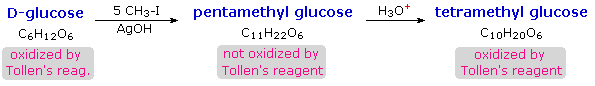
When glucose was converted to its pentamethyl ether (reaction with excess CH3I & AgOH), two different isomers were isolated, and neither exhibited the expected aldehyde reactions. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of the pentamethyl ether derivatives, however, gave a tetramethyl derivative that was oxidized by Tollen's reagent and reduced by sodium borohydride, as expected for an aldehyde. These reactions will be displayed above.
The search for scientific truth often proceeds in stages, and the structural elucidation of glucose serves as a good example. It should be clear from the new evidence presented above, that the open chain pentahydroxyhexanal structure drawn above must be modified. Somehow a new stereogenic center must be created, and the aldehyde must be deactivated in the pentamethyl derivative. A simple solution to this dilemma is achieved by converting the open aldehyde structure for glucose into a cyclic hemiacetal, called a glucopyranose, as shown in the following diagram. The linear aldehyde is tipped on its side, and rotation about the C4-C5 bond brings the C5-hydroxyl function close to the aldehyde carbon. For ease of viewing, the six-membered hemiacetal structure is drawn as a flat hexagon, but it actually assumes a chair conformation. The hemiacetal carbon atom (C-1) becomes a new stereogenic center, commonly referred to as the anomeric carbon, and the α and β-isomers are called anomers.
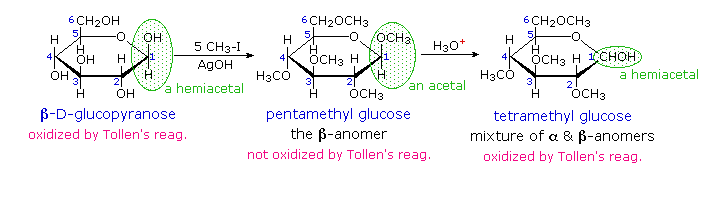
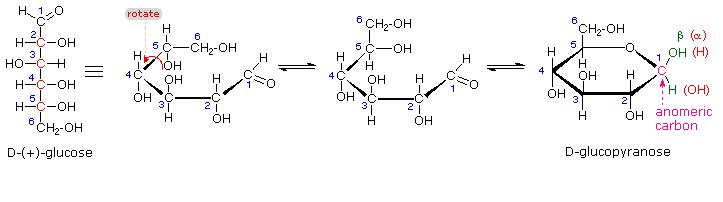
We can now consider how this modification of the glucose structure accounts for the puzzling facts noted above. First, we know that hemiacetals are in equilibrium with their carbonyl and alcohol components when in solution. Consequently, fresh solutions of either alpha or beta-glucose crystals in water should establish an equilibrium mixture of both anomers, plus the open chain chain form. Note that despite the very low concentration of the open chain aldehyde in this mixture, typical chemical reactions of aldehydes take place rapidly.
Second, a pentamethyl ether derivative of the pyranose structure converts the hemiacetal function to an acetal. Acetals are stable to base, so this product should not react with Tollen's reagent or be reduced by sodium borohydride. Acid hydrolysis of acetals regenerates the carbonyl and alcohol components, and in the case of the glucose derivative this will be a tetramethyl ether of the pyranose hemiacetal. This compound will, of course, undergo typical aldehyde reactions. this relationship is displayed above.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|