


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 19-1-2018
Date: 10-1-2019
Date: 1-2-2018
|
The hydrogen ion (proton)
The ionization energy of hydrogen (defined for reaction 1.1) is 1312 kJ mol‑1, a value that is high enough to preclude the existence of H+ ions under ordinary conditions.
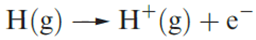 (1.1)
(1.1)
However, as we discussed in Chapter 6, the hydrated proton or oxonium ion, [H3O]+, is an important species in aqueous solution; ΔhydHo)H;g( = _1091 kJ mol_1 (see Section 6.9). The [H3O]+ ion (1.1) is a well-defined species which has been crystallographically characterized in various salts. The ions [H5O2] (Figure 1.1) and ½H9O4_ have also been isolated in crystalline acid hydrates. The [H5O2] and [H9O4] ions are members of the general family of hydrated protons [H(H2O)n] (n =1 to ≈ 20) and we return to these ions when we discuss hydrogen bonding in Section 9.6.
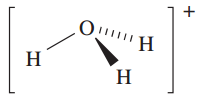
(1.1)
When crystals of a compound are grown from a solvent, they may contain solvent of crystallization; if the solvent is water, the compound is a hydrate. The formula of the solvated compound shows the molar ratio in which the solvent of crystallization is present, e.g. CuSO4.5H2O, copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate or copper(II) sulfate–water (1/5).
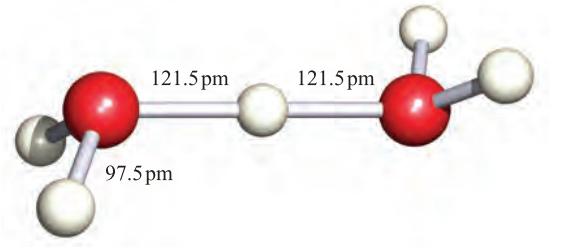
Fig. 1.1 The structure of [H5O2]+ determined by neutron diffraction in the compound [V(H2O) 6][H5O2][CF3SO3]4. [F.A. Cotton et al. (1984) J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 106, p. 5319.]



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أولياء أمور الطلبة يشيدون بمبادرة العتبة العباسية بتكريم الأوائل في المراحل المنتهية
|
|
|