


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 8-8-2016
Date: 11-8-2016
Date: 13-7-2016
|
Loop in Magnetic Field
A conducting circular loop made of wire of diameter d, resistivity ρ, and mass density ρm is falling from a great height h in a magnetic field with a component Bz = B0(1+ kz), where k is some constant. The loop of diameter D is always parallel to the x-y plane. Disregarding air resistance, find the terminal velocity of the loop (see Figure 1.1).

Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
The magnetic force acting on the loop is proportional to its magnetic moment, which is proportional to the current flowing through the loop. The current I, in turn, is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop, since I = εe/R, where εe is the electromotive force and R is the resistance of the loop. We have

The magnetic flux Φ in (1) is given by
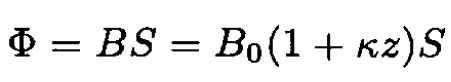 (2)
(2)
where S is the area of the loop. From (1),
 (3)
(3)
But dz/dt is the velocity of the loop. So the electromotive force increases with the velocity, and therefore the magnetic force Fm acting on the loop also increases with velocity, while the only other force, gravity, acting in the opposite direction, is constant. Therefore, the velocity will increase until Fm = mg From energy conservation, the work done by gravity during this stationary motion goes into the Joule heating of the loop:
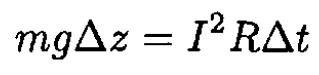 (4)
(4)
But, since the velocity is constant,
 (5)
(5)
where we substituted εe from (3) again using v = dz/dt. From (5), we can find
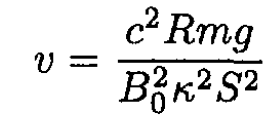 (6)
(6)
Now, substituting
 (7)
(7)
and
 (8)
(8)
into (6), we obtain




|
|
|
|
هل يمكن أن تكون الطماطم مفتاح الوقاية من السرطان؟
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف عرائس"غريبة" عمرها 2400 عام على قمة هرم بالسلفادور
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تقيم ندوة علمية عن الاعتماد الأكاديمي في جامعة جابر بن حيّان
|
|
|