


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 4-9-2020
Date: 7-6-2019
Date: 27-7-2020
|
The heavy orange zigzag line running diagonally from the upper left to the lower right through groups 13–16 in Figure 1.1
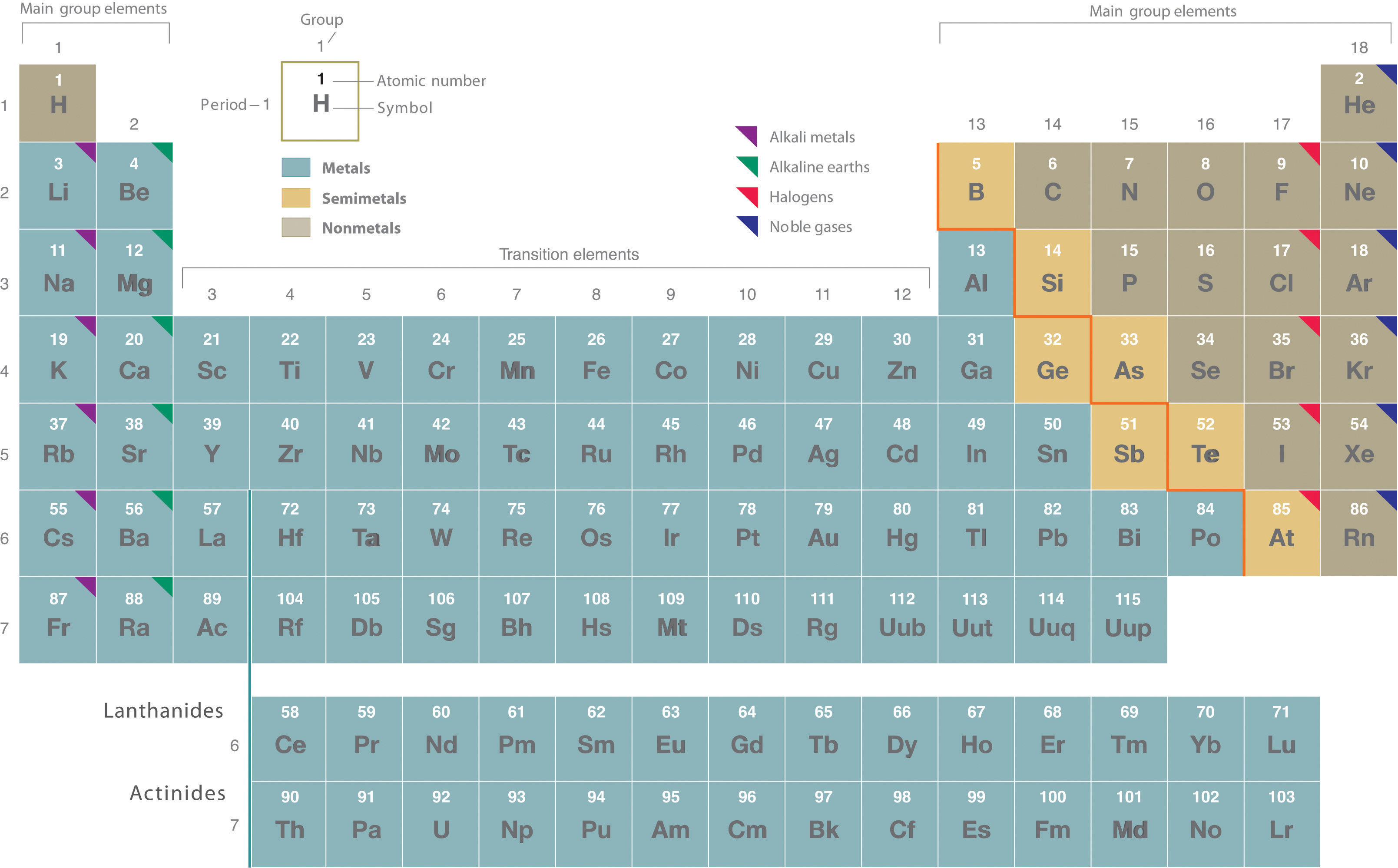
Figure 1.1 : The Periodic Table Showing the Elements in Order of Increasing Z. The metals are on the bottom left in the periodic table, and the nonmetals are at the top right. The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals.
divides the elements into metals (in blue, below and to the left of the line) and nonmetals (in bronze, above and to the right of the line). Gold-colored lements that lie along the diagonal line exhibit properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals; they are called semimetals.
The distinction between metals and nonmetals is one of the most fundamental in chemistry. Metals—such as copper or gold—are good conductors of electricity and heat; they can be pulled into wires because they are ductile; they can be hammered or pressed into thin sheets or foils because they are malleable; and most have a shiny appearance, so they are lustrous. The vast majority of the known elements are metals. Of the metals, only mercury is a liquid at room temperature and pressure; all the rest are solids.
Nonmetals, in contrast, are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity and are not lustrous. Nonmetals can be gases (such as chlorine), liquids (such as bromine), or solids (such as iodine) at room temperature and pressure. Most solid nonmetals are brittle, so they break into small pieces when hit with a hammer or pulled into a wire. As expected, semimetals exhibit properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals.
Example : Classifying Elements
Based on its position in the periodic table, do you expect selenium to be a metal, a nonmetal, or a semimetal?
Given: element
Asked for: classification
Strategy:
Find selenium in the periodic table shown in Figure 1.1
and then classify the element according to its location.
Solution:
The atomic number of selenium is 34, which places it in period 4 and group 16. In Figure 1.1
, selenium lies above and to the right of the diagonal line marking the boundary between metals and nonmetals, so it should be a nonmetal. Note, however, that because selenium is close to the metal-nonmetal dividing line, it would not be surprising if selenium were similar to a semimetal in some of its properties.
Exercise :
Based on its location in the periodic table, do you expect indium to be a nonmetal, a metal, or a semimetal?
Answer
As previously noted, the periodic table is arranged so that elements with similar chemical behaviors are in the same group. Chemists often make general statements about the properties of the elements in a group using descriptive names with historical origins. For example, the elements of Group 1 are known as the alkali metals, Group 2 are the alkaline earth metals, Group 17 are the halogens, and Group 18 are the noble gases.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|