


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 13-8-2020
Date: 29-7-2020
Date: 6-9-2020
|
The study of chemical reactions, isomerizations and physical behavior that may occur under the influence of visible and/or ultraviolet light is called Photochemistry. Two fundamental principles are the foundation for understanding photochemical transformations:
• The first law of photochemistry, the Grotthuss-Draper law, states that light must be absorbed by a compound in order for a photochemical reaction to take place.
• The second law of photochemistry, the Stark-Einstein law, states that for each photon of light absorbed by a chemical system, only one molecule is activated for subsequent reaction. This "photoequivalence law" was derived by Albert Einstein during his development of the quantum (photon) theory of light.
efficiency with which a given photochemical process occurs is given by its Quantum Yield (Φ). Since many photochemical reactions are complex, and may compete with unproductive energy loss, the quantum yield is usually specified for a particular event. Thus, we may define quantum yield as "the number of moles of a stated reactant disappearing, or the number of moles of a stated product produced, per einstein of monochromatic light absorbed.", where an einstein is one mole of photons. For example, irradiation of acetone with 313 nm light (3130 Å ) gives a complex mixture of products, as shown in the following diagram. The quantum yield of these products is less than 0.2, indicating there are radiative (fluorescence & phosphorescence) and non-radiative return pathways (green arrow). The primary photochemical reaction is the homolytic cleavage of a carbon-carbon bond shown in the top equation. Here the asterisk represents an electronic excited state, the nature of which will be defined later.
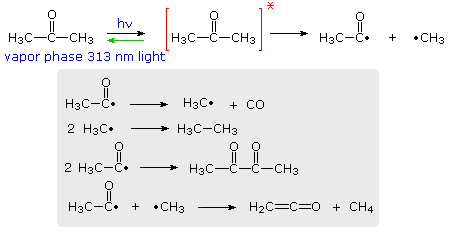
Several secondary radical reactions then follow (shown in the gray box), making it difficult to assign a quantum yield to the primary reaction. The biacetyl product, formed in the third reaction, may itself be excited by light or accept excitation energy from an excited acetone molecule, further complicating this process.
By comparison, the light induced chlorination of methane, or other alkanes, has a large quantum yield, often near 106, because of the secondary chain reactions that follow the primary cleavage of the Cl-Cl bond.



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|