


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 8-1-2017
Date: 15-1-2017
Date: 2-8-2016
|
Embryonic Hyaline Cartilage
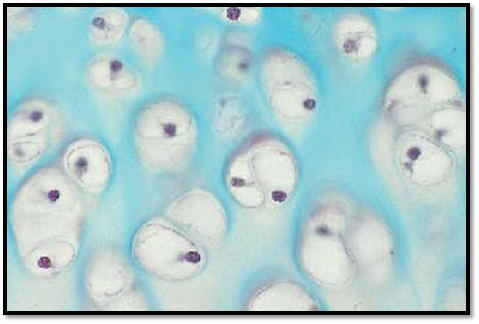
Hyaline cartilage develops from mesenchymal blastema. Mesenchyme cells differentiate into cartilage-forming cells, the chondroblasts, and in turn, these differentiate into cartilage cells, the chondrocytes . Chondroblasts synthesize the cartilage ground substance ( cartilage matrix), which consists of water, glycosaminoglycans and collagen fibrils (type II collagen ). The collagen fibrils are masked by components of the ground substance—i.e., by materials in the extracellular matrix. Chondroblasts release their products in all directions and consequently wall themselves in. In the process, they turn into chondrocytes, which rest in the smooth-walled caverns of the cartilage matrix (cartilage caverns, lacunae). Even while they are enclose d, chondrocytes will still divide, thus forming isogenous groups of cartilage cells (interstitial or intussusceptional growth ). The figure shows large round chondrocytes singly or as groups: chondrons or territories. The space between them is filled with cartilage ground substance: interterritorial extracellular matrix . Iliac tissue from a human fetus, 5th gestational month. Note the spherical chondrocytes with small nuclei (stained blue-violet) and the remarkably light cytoplasm.
Stain: Masson-Goldner trichrome staining; magnification: × 400
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|