

 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 8-10-2020
Date: 21-2-2021
Date: 5-3-2021
|
Quantum phase transitions
Quantum phase transitions take place at 0 K, unlike normal phase transitions which occur as a function of temperature, driven by the greater entropy of the high-temperature phase. An electronic phase transition as a function of composition x or gate voltage, or a magnetic phase transition as a function of J0/ΔJ (Fig. 1) may be examples of a quantum phase transition. Magnetic field or pressure are the easiest variables to control in the laboratory. In any case, by tuning some variable g one may enter a region where two states compete to be the ground state of the system. In quantum systems, fluctuations like those described by the uncertainty principle are always present.
An example is the compound LiHoF4, where the Ho3+ ion sits in a site with uniaxial anisotropy which stabilizes an MJ = ±8 doublet, giving the ion an Ising-like character. Weak coupling between the Ho3+ ions causes the compound to order ferromagnetically at 1.6 K. A field applied perpendicular to the axis causes tunnelling between the two states, and eventually destroys the ferromagnetic order, creating a quantum paramagnet.
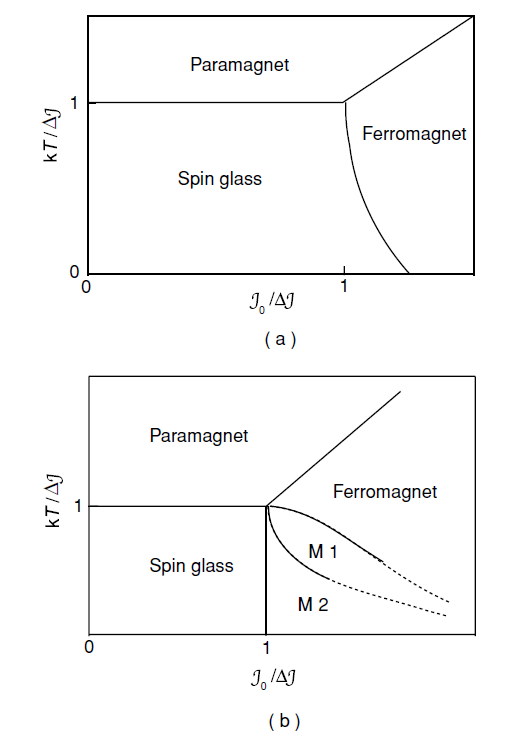
Figure 1: Theoretical phase diagrams calculated in mean field theory for (a) an Ising spin glass by D. Sherrington and S. Kirkpatrick (Phys. Rev. Letters 35, 1792 (1975)) and (b) for vector spins by M. Gabay and G. Toulouse (Phys. Rev. Letters 47, 201 (1981)). There is a distribution of exchange of width Δ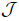 and average value J0.
and average value J0.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|