


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 27-8-2018
Date: 27-12-2019
Date: 24-8-2018
|
The five bases that are found in nucleotides are often represented by their initial letter: adenine, A; guanine, G; cytosine, C; thymine, T; and uracil, U. Note that A, G, C and T occur in DNA; A, G, C and U occur in RNA. You are not required to memorize the structures of these bases, but you must know how each one bonds to the sugar unit in a nucleotide. To fulfill Objective 6, you should be able to reproduce the figure below.
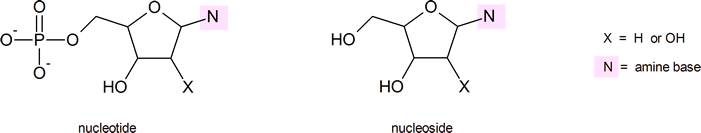
To fulfill Objective 7, you should study (but not necessarily memorize) Figure 1.2 The Pyrimidine and Purine Nucleotides below.
The Learning Objective of this Module is to identify the different molecules that combine to form nucleotides.
The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. The deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a typical mammalian cell contains about 3 × 109 nucleotides. Nucleotides can be further broken down to phosphoric acid (H3PO4), a pentose sugar (a sugar with five carbon atoms), and a nitrogenous base (a base containing nitrogen atoms).
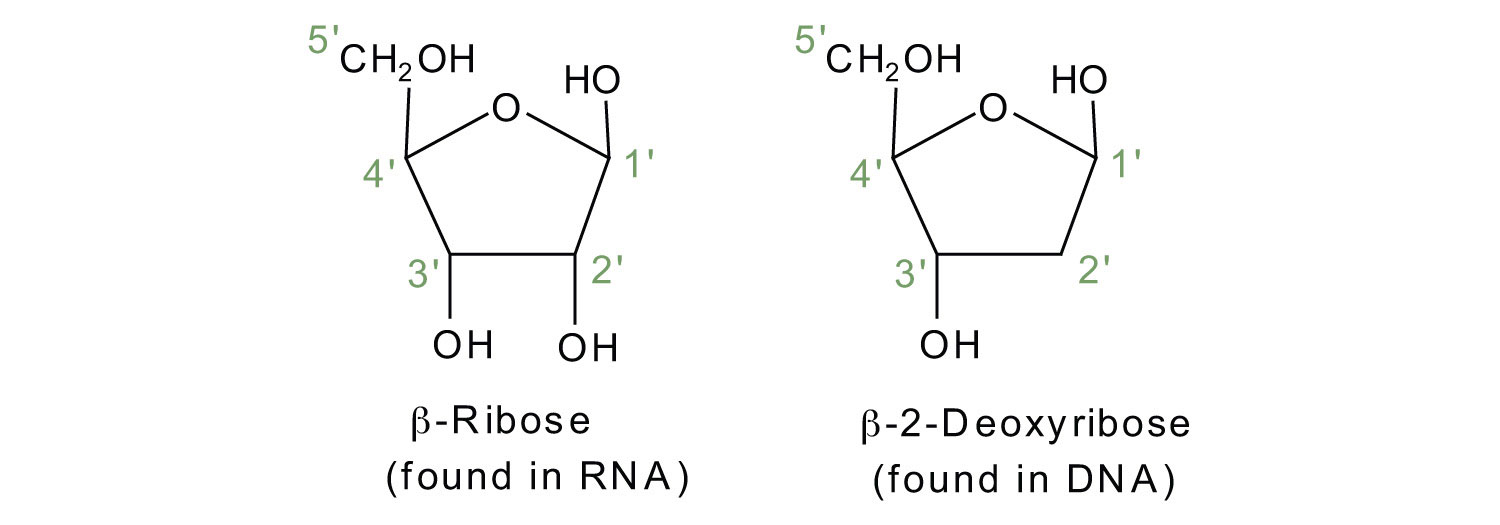
If the pentose sugar is ribose, the nucleotide is more specifically referred to as a ribonucleotide, and the resulting nucleic acid is ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is 2-deoxyribose, the nucleotide is a deoxyribonucleotide, and the nucleic acid is DNA.
The nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides are classified as pyrimidines or purines. Pyrimidines are heterocyclic amines with two nitrogen atoms in a six-member ring and include uracil, thymine, and cytosine. Purines are heterocyclic amines consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to a five-member ring with two nitrogen atoms. Adenine and guanine are the major purines found in nucleic acids (Figure 1.1).
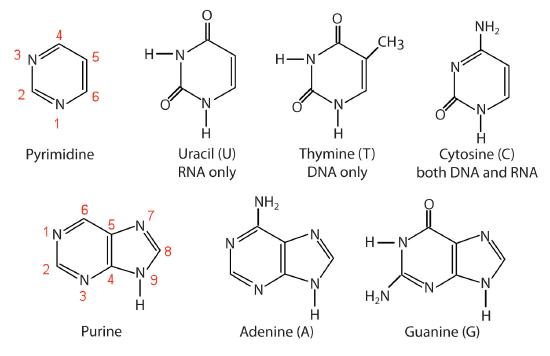
Figure 1.1: The Nitrogenous Bases Found in DNA and RNA
The formation of a bond between C1′ of the pentose sugar and N1 of the pyrimidine base or N9 of the purine base joins the pentose sugar to the nitrogenous base. In the formation of this bond, a molecule of water is removed. Table 1.1 summarizes the similarities and differences in the composition of nucleotides in DNA and RNA.
Example
The numbering convention is that primed numbers designate the atoms of the pentose ring, and unprimed numbers designate the atoms of the purine or pyrimidine ring.
| Composition | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| purine bases | adenine and guanine | adenine and guanine |
| pyrimidine bases | cytosine and thymine | cytosine and uracil |
| pentose sugar | 2-deoxyribose | ribose |
| inorganic acid | phosphoric acid (H3PO4) | H3PO4 |
The names and structures of the major ribonucleotides and one of the deoxyribonucleotides are given in Figure 1.2.
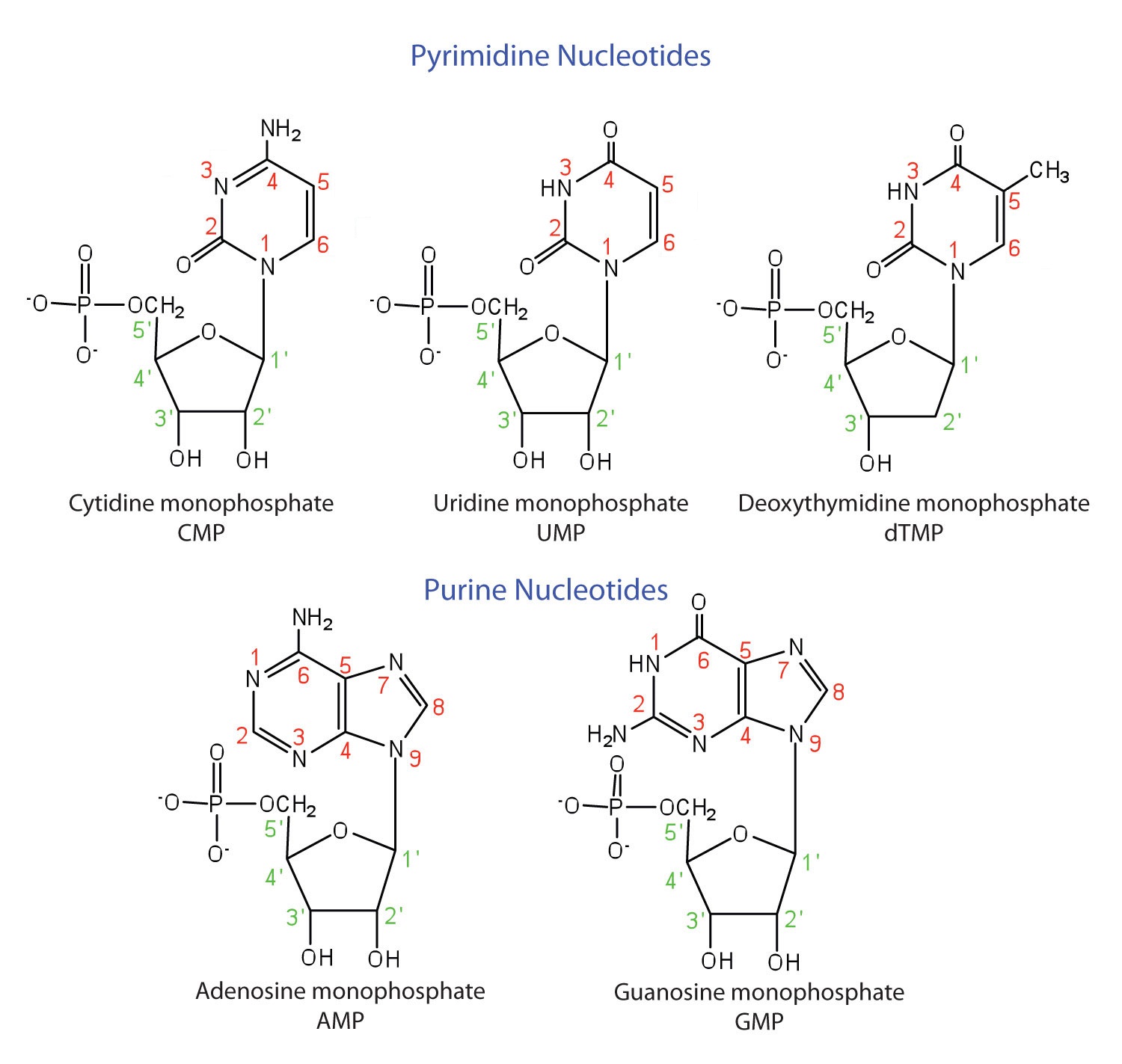
Figure 1.2 The Pyrimidine and Purine Nucleotides
Apart from being the monomer units of DNA and RNA, the nucleotides and some of their derivatives have other functions as well. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), shown in Figure 1.3, have a role in cell metabolism. Moreover, a number of coenzymes, including flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), and coenzyme A, contain adenine nucleotides as structural components.
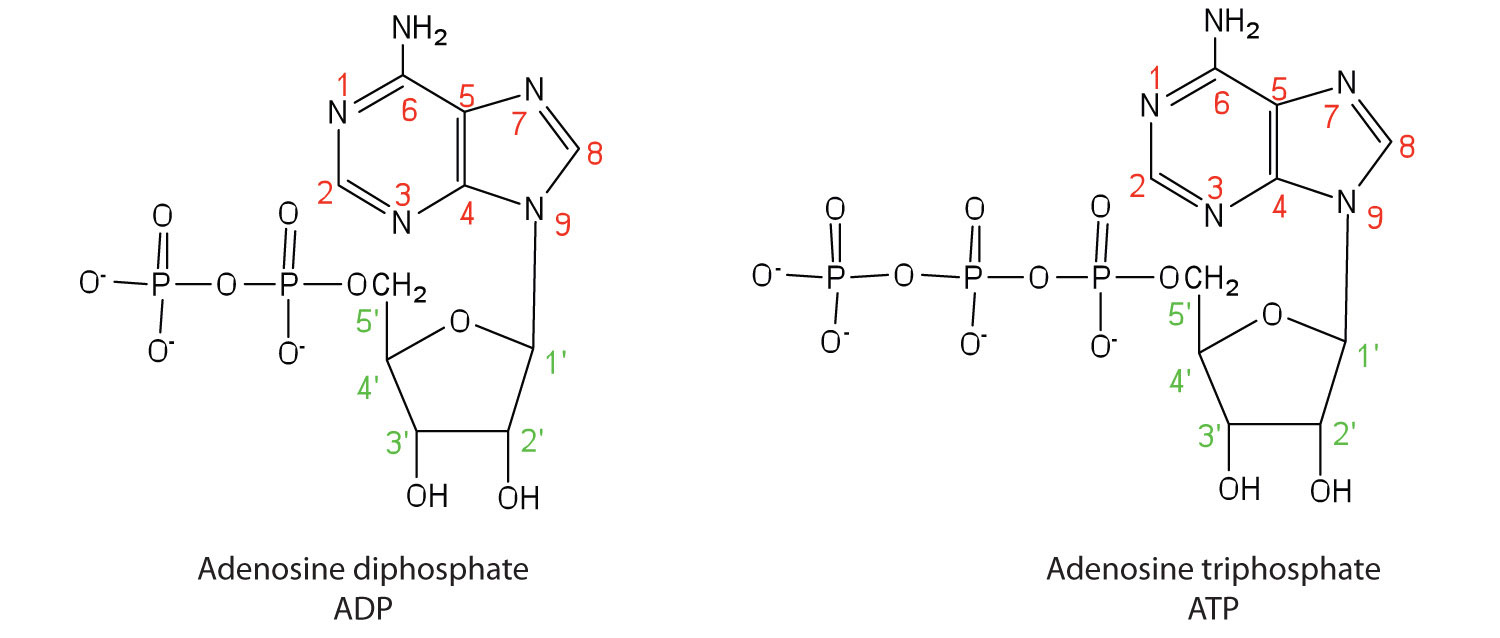
Figure 1.3: Structures of Two Important Adenine-Containing Nucleotides



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|