


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 9-9-2019
Date: 7-9-2019
Date: 14-12-2020
|
Examples
Ethane: CH3CH3 ----->Ethanol:
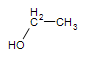
(the alcohol found in beer, wine and other consumed sprits)
Secondary alcohol:
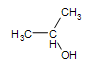
2-propanol
Other functional groups on an alcohol: 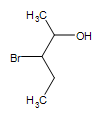 3-bromo-2-pentanol
3-bromo-2-pentanol
Cyclic alcohol (two -OH groups):
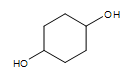
cyclohexan-1,4-diol
Other functional group on the cyclic structure:
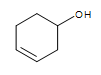
3-hexeneol (the alkene is in bold and indicated by numbering the carbon closest to the alcohol)
A complex alcohol:
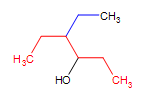
4-ethyl-3hexanol (the parent chain is in red and the substituent is in blue)
In the IUPAC system of nomenclature, functional groups are normally designated in one of two ways. The presence of the function may be indicated by a characteristic suffix and a location number. This is common for the carbon-carbon double and triple bonds which have the respective suffixes -ene and -yne. Halogens, on the other hand, do not have a suffix and are named as substituents, for example: (CH3)2C=CHCHClCH3 is 4-chloro-2-methyl-2-pentene.
Alcohols are usually named by the first procedure and are designated by an -ol suffix, as in ethanol, CH3CH2OH (note that a locator number is unnecessary on a two-carbon chain). On longer chains the location of the hydroxyl group determines chain numbering. For example: (CH3)2C=CHCH(OH)CH3 is 4-methyl-3-penten-2-ol. Other examples of IUPAC nomenclature are shown below, together with the common names often used for some of the simpler compounds. For the mono-functional alcohols, this common system consists of naming the alkyl group followed by the word alcohol. Alcohols may also be classified as primary, 1º, secondary, 2º, and tertiary, 3º, in the same manner as alkyl halides. This terminology refers to alkyl substitution of the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group (colored blue in the illustration).
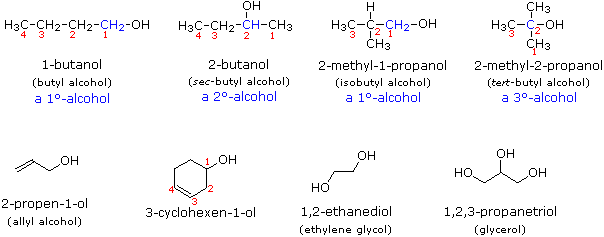
Many functional groups have a characteristic suffix designator, and only one such suffix (other than "-ene" and "-yne") may be used in a name. When the hydroxyl functional group is present together with a function of higher nomenclature priority, it must be cited and located by the prefix hydroxy and an appropriate number. For example, lactic acid has the IUPAC name 2-hydroxypropanoic acid.



|
|
|
|
حمية العقل.. نظام صحي لإطالة شباب دماغك
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
إيرباص تكشف عن نموذج تجريبي من نصف طائرة ونصف هليكوبتر
|
|
|
|
|
|
اختتام الأسبوع الثاني من الشهر الثالث للبرنامج المركزي لمنتسبي العتبة العباسية
|
|
|
|
راية قبة مرقد أبي الفضل العباس (عليه السلام) تتوسط جناح العتبة العباسية في معرض طهران
|
|
|
|
جامعة العميد وقسم الشؤون الفكرية يعقدان شراكة علمية حول مجلة (تسليم)
|
|
|
|
قسم الشؤون الفكريّة يفتتح باب التسجيل في دورات المواهب
|