
Geometric Isomerism
 المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
 المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
 الجزء والصفحة:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
 26-12-2021
26-12-2021
 3049
3049
Geometric Isomerism
We have defined isomers in a very general way as nonidentical molecules that possess the same number and kind of atoms. However, there are several ways in which isomers can be nonidentical. Among the alkenes, 1- and 2-butene are position isomers, because in these compounds the double bond has a different position in the carbon chain:
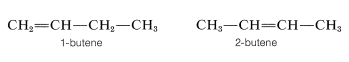
Most, but not all alkenes, have stereoisomers that are not identical because of different spatial arrangements of the component atoms. Thus there are two stereoisomers of 2-butene that differ in the geometric arrangement of the groups attached to the double bond. In one isomer, both methyl groups are on the same side of the double bond (cis-2-butene) and in the other, the methyl groups are on opposite sides of the double bond (trans-2-butene):

Figure 5-1, and the rigidity of the double bond is simulated in the model by a pair of stiff springs or bent sticks connecting the two carbons of the double bond.
It should be clear to you that there will be no cis-trans isomers of alkenes in which one end of the double bond carries identical groups. Thus we don not expect there to be cis-trans isomers of 1-butene or 2-methylpropene, and

Figure 5-1: Ball-and-stick models of cis- and trans-2-butene indeed none are known:
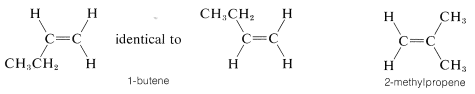
You may wish to verify this by making ball-and-stick models of these substances.
Ring formation also confers rigidity on molecular structure such that rotation about the ring bonds is prevented. As a result, stereoisomerism of the cis-trans type is possible. For example, 1,2-dimethylcyclopropane exists in two forms that differ in the arrangement of the two methyl groups with

Figure 5-2: Ball-and-stick models of cis and trans isomers of 1,2-dimethylcyclopropane
respect to the ring. In the cis isomer, the methyl groups both are situated above (or below) the plane of the ring and in the trans isomer they are situated one above and one below, as shown in Figure 5-2. Interconversion of these isomers does not occur without breaking one or more chemical bonds.
Stereoisomers that do not interconvert rapidly under normal conditions, and therefore are stable enough to be separated, specifically are called configurational isomers. Thus cis- and trans-2-butene are configurational isomers, as are cis- and trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane. The terms cis-trans isomerism or geometric isomerism commonly are used to describe configurational isomerism in compounds with double bonds and rings. When referring to the configuration of a particular isomer, we mean to specify its geometry. For instance, the isomer of 1,2-dichloroethene shown below has the trans configuration; the isomer of 1,3-dichlorocyclobutane has the cis configuration:
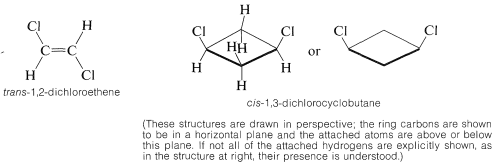
Cis-trans isomerism is encountered very frequently. By one convention, the configuration of a complex alkene is taken to correspond to the configuration of the longest continuous chain as it passes through the double bond. Thus the following compound is trans-4-ethyl-3-methyl-3-heptene, despite the fact that two identical groups are cis with respect to each other, because the longest continuous chain is trans as it passes through the double bond:
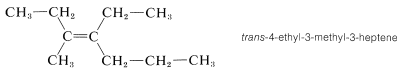
Notice that cis-trans isomerism is not possible at a carbon-carbon triple bond, as for 2-butyne, because the bonding arrangement at the triply bonded carbons is linear:

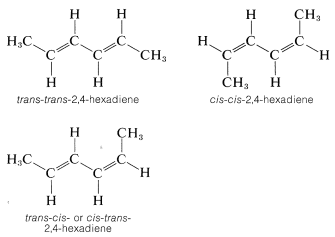
Many compounds have more than one double bond and each may have the potential for the cis or trans arrangement. For example, 2,4-hexadiene has three different configurations, which are designated as trans-trans, cis-cis, and trans-cis. Because the two ends of this molecule are identically substituted, the trans-cis becomes identical with cis-trans:
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


