
Cumene
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 269
الجزء والصفحة:
p 269
 10-9-2017
10-9-2017
 3059
3059
Cumene
Cumene (isopropylbenzene), a liquid, is soluble in many organic solvents but not in water. It is present in low concentrations in light refinery streams (such as reformates) and coal liquids. It may be obtained by distilling (cumene’s B.P. is 152.7°C) these fractions.
The main process for producing cumene is a synthetic route where benzene is alkylated with propylene to isopropylbenzene.
Either a liquid or a gas-phase process is used for the alkylation reaction. In the liquid-phase process, low temperatures and pressures (approximately 50°C and 5 atmospheres ) are used with sulfuric acid as a catalyst.
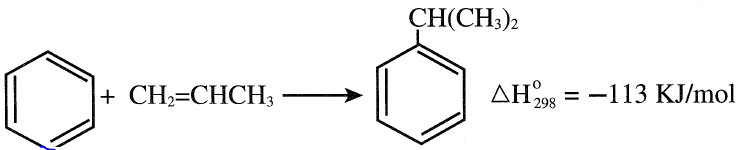
Small amounts of ethylene can be tolerated since ethylene is quite unreactive under these conditions. Butylenes are relatively unimportant because butylbenzene can be removed as bottoms from the cumene column.
In the vapor-phase process, the reaction temperature and pressure are approximately 250°C and 40 atmospheres. Phosphoric acid on Kieselguhr is a commonly used catalyst. To limit polyalkylation, a mixture of propene-propane feed is used. Propylene can be as low as 40% of the feed mixture. Ahigh benzene/propylene ratio is also used to decrease polyalkylation.
A selectivity of about 97% based on benzene can be obtained. In the UOP process (Figure 1.1), fresh propylene feed is combined with fresh and recycled benzene, then passed through heat exchangers and a steam preheater before being charged to the reactor. The effluent is separated, and excess benzene recycled. Cumene is finally clay treated and fractionated. The bottom product is mainly diisopropyl benzene, which is reacted with benzene in a transalkylation section:
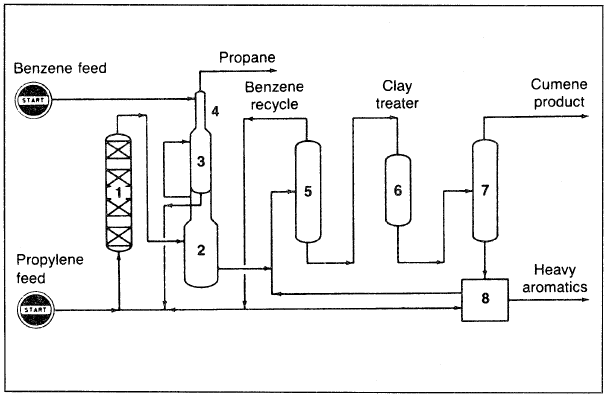
Figure 1.1. A flow diagram of the UOP cumene process: (1) reactor, (2,3) twostage flash system, (4) depropanizer, (5) benzene column, (6) clay treatment, (7) fractionator, (8) transalkylation section.

To reduce pollution, Dow developed a new catalyst system from the mordenite-zeolite group to replace phosophoric acid or aluminum chloride catalysts. The new catalysts eliminates the disposal of acid wastes and handling corrosive materials.
The 1998 U.S. cumene production was approximately 6.7 billion pounds and was mainly used to produce phenol and acetone. A small amount of cumene is used to make α-methylstyrene by dehydrogenation.
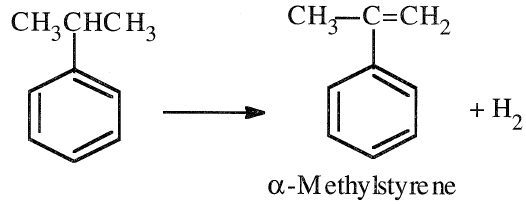
α-Methylstyrene is used as a monomer for polymer manufacture and as a solvent.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


