


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 29-10-2020
Date: 12-12-2016
Date: 6-2-2021
|
Line integrals
Consider a two-dimensional function f(x, y) which is defined for all x and y. What is meant by the integral of f along a given curve from P to Q in the x-y
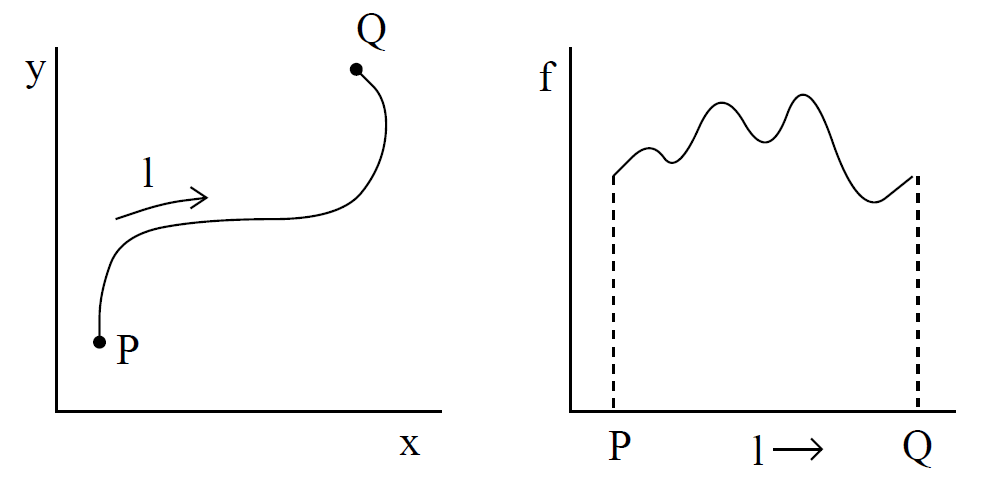
plane? We first draw out f as a function of length l along the path. The integral is then simply given by
 (1.1)
(1.1)
As an example of this, consider the integral of f(x, y) = xy between P and Q along the two routes indicated in the diagram below. Along route 1 we have
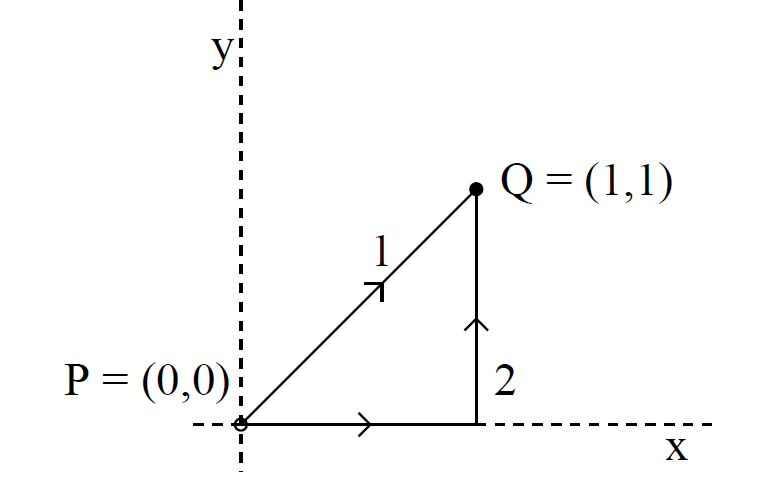
x = y, so dl = 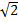 dx. Thus,
dx. Thus,
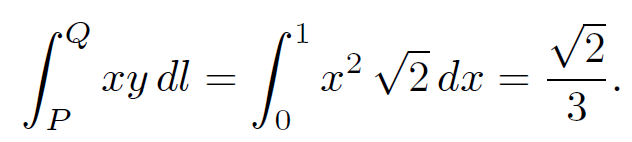 (1.2)
(1.2)
The integration along route 2 gives
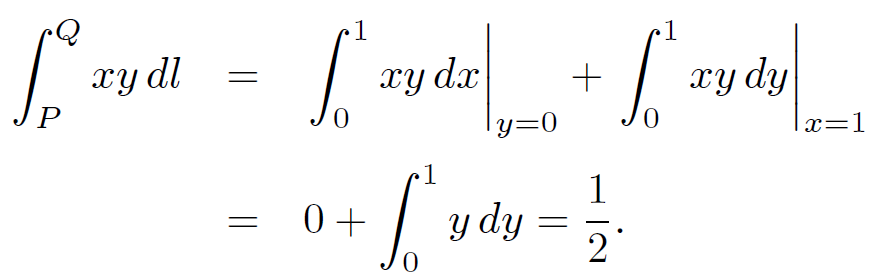 (1.3)
(1.3)
Note that the integral depends on the route taken between the initial and final points. The most common type of line integral is where the contributions from dx and dy are evaluated separately, rather that through the path length dl;
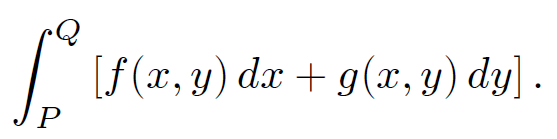 (1.4)
(1.4)
As an example of this consider the integral
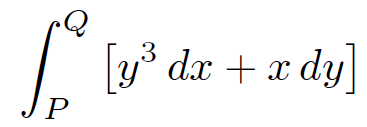 (1.5)
(1.5)
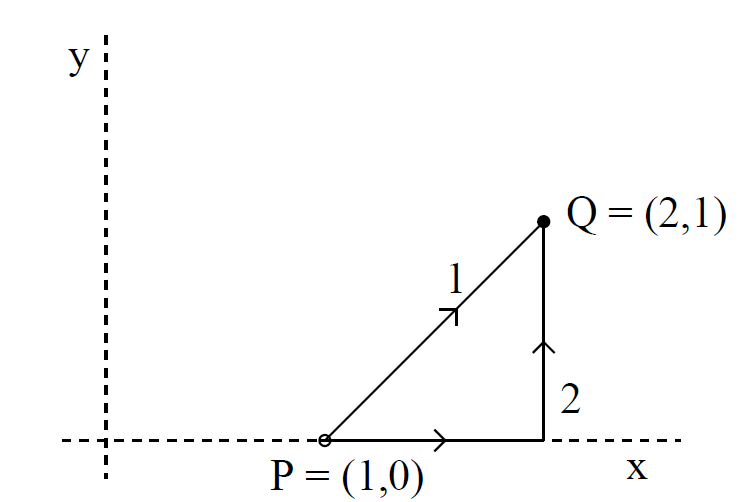
along the two routes indicated in the diagram below. Along route 1 we have x = y + 1 and dx = dy, so
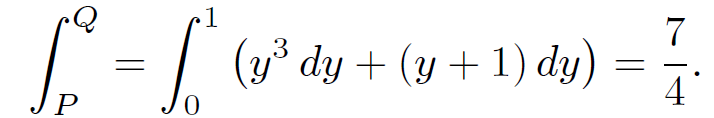 (1.6)
(1.6)
Along route 2
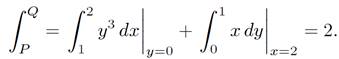 (1.7)
(1.7)
Again, the integral depends on the path of integration. Suppose that we have a line integral which does not depend on the path of integration. It follows that
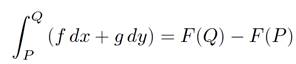 (1.8)
(1.8)
for some function F. Given F(P) for one point P in the x-y plane, then
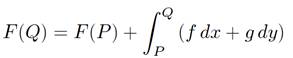 (1.9)
(1.9)
defines F(Q) for all other points in the plane. We can then draw a contour map of F(x, y). The line integral between points P and Q is simply the change in height in the contour map between these two points:
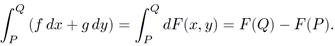 (1.10)
(1.10)
Thus,
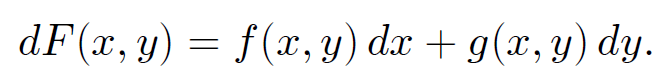 (1.11)
(1.11)
For instance, if F = xy3 then dF = y3 dx + 3xy2 dy and
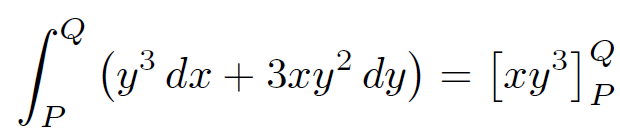 (1.12)
(1.12)
is independent of the path of integration. It is clear that there are two distinct types of line integral. Those that depend only on their endpoints and not on the path of integration, and those which depend both on their endpoints and the integration path. Later on, we shall learn how to distinguish between these two types.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|