


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات | INTRODUCTION TO PROBABILITY IN FINITE SAMPLE SPACES-Some aids to counting |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 10-1-2017
Date: 29-12-2016
Date: 5-1-2017
|
The question of how one should proceed to count the number of elements in a set is not, strictly speaking, a part of the algebra of sets. However, to demonstrate how the algebra of sets forms the basis of probability theory, we would like to investigate sample spaces of a more involved nature. To do so requires the use of the theory of permutations and combinations. This theory is essentially a counting technique, and will be discussed briefly for the benefit of readers who may not have the necessary background. Anyone familiar with this material may easily proceed to (Bernoulli trials, binomial distribution).
First, we shall define an ordered pair to be a special kind of set containing exactly two elements, with the additional property that we are able to distinguish one of the elements, called the first element, from the other, called the second element. We shall designate such pairs (x, y), where x is the first element, and y is the second element. A fundamental principle of counting is the following:
If X and Y are any two sets with finitely many elements, the number of distinct ordered pairs (x, y) which can be formed with x ∈ X and y∈Y is n(X)n(Y).
The concept of ordered pairs is easily extended to the concept of ordered r-tuples, each of which is a set with exactly r elements, with the property that it is possible to determine uniquely a first, second, ... , rth element. Such r-tuples are denoted by (X1, x2, ... , xr). The fundamental principle extends to give the number of distinct r-tuples as the product of the numbers of elements which may be used for the respective positions.
DEFINITION. The number of permutations of n things taken r at a time, 0 ≤ r≤n, is defined to be the number of distinct r-tuples which can be formed from n elements, where it is assumed that no element can simultaneously appear twice in one r-tuple. This number is denoted by ,nPr.
THEOREM 1. The value of nPr is given by
nPr=n(n-1)(n-2)...(n-r-1) (1)
Proof. If we consider the definition of nPr, it is clear that the first element of the r-tuple is to be chosen from a set of n elements. Having chosen the first element, a set of n - 1 elements is left, from which the second may be chosen, etc. Hence the formula follows.
In the case r = n, Theorem 1 says that there are n(n - 1) (n - 2) (2)(1) permutations of n things taken n at a time. This number appears so often that it is convenient to give it a special designation, n!. We will extend the definition of this symbol to the special case n = 0 by defining 0! to be the number 1. Using this new notation, Eq. (1) can also be written as

DEFINITION. The number of combinations of n things taken r at a time is defined to be the number of distinct subsets, each containing r elements, which are contained in a set with n elements. We denote this number by (nr).
THEOREM 2. The value of (nr) is given by

Proof. Clearly the distinction between the numbers .nPr and (nr)is that (nr)counts subsets only, whereas nPr counts each possible ordering within each subset. Hence the relation between the numbers is

This follows since, after a subset has been chosen, it may still be arranged in r! ways, by Theorem 1. If nPr in Eq. (4) is replaced by n!/(n - r) ! and both sides of the resulting equation are divided by r!, Eq. (3) is obtained. In any particular problem, before these formulas are used, care must be taken to determine whether permutations or combinations are required.
Although no rules can be formulated to replace intelligent thinking, a guide to the correct choice is the decision as to whether "order" is important. In selecting a committee of three, where no significance is attached to being first, second, or third, it would be natural to use the idea of combinations. If, however, the first choice were to be chairman and the second choice secretary, it might be more natural to use the idea of permutations. That is, in this case we would consider the committee Jones, president; Smith, secretary; and Brown as distinct from the committee Brown, president; Smith, secretary; and Jones.
EXAMPLE 1. How many distinct numbers of four digits, each having no repeated digits, can be formed from the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7?
Solution. The number is 7P4 = 7!/3! = 840.
EXAMPLE 2. How many different sums of money can be formed from one penny, one nickel, one dime, one quarter, and one half dollar?
Solution. Here order makes no difference, hence the answer is
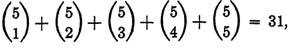
EXAMPLE 3. Find the probability that a five-card poker hand will be a straight flush (five cards in sequence in a single suit, but not with ace high; the ace may be used as low card, however).
Solution. First, the choices of suit and of possible hands within a suit may be thought of as the choice of pairs of elements, the first from the set of suits, the second from the set of allowable hands within suits, and hence the basic principle of counting may be applied. There are four possible suits, and a permissible hand may have as low card any of the nine cards A, 2, 3, ..., 9. The total number of five-card hands (corresponding to the number of elements in the sample space) is (525 ). Hence the desired probability is (4) (9)/(525), or approximately 0.000,014.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|