


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 10-10-2016
Date: 7-10-2016
Date: 10-11-2016
|
Cosmic Background Radiation
Cosmic background radiation was first detected in the microwave region in the 1960s and exhibits a perfect blackbody spectrum equivalent to the radiation from a source at a temperature of 2.72 K. One would expect
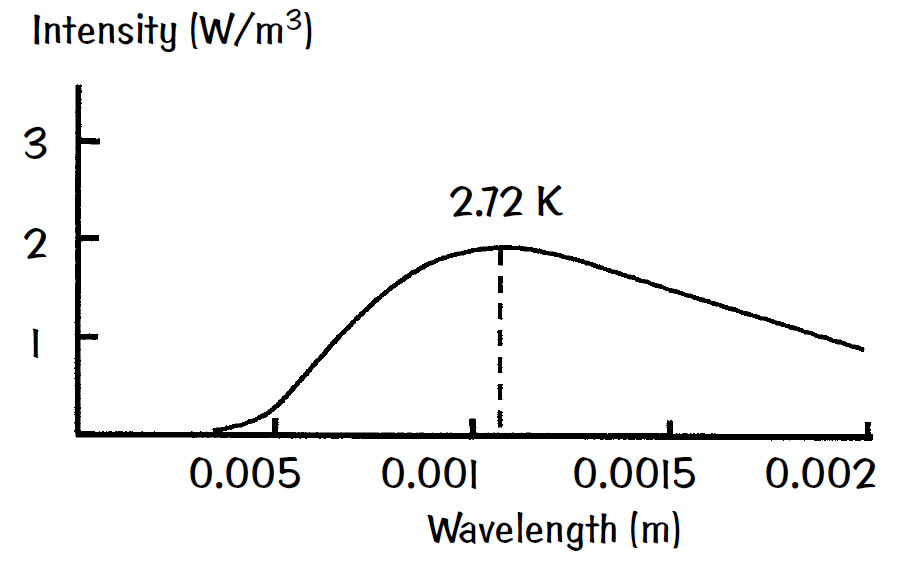
lots of remnant starlight all over the universe in all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum emitted for the past 10 billion years or so. Yet this microwave background radiation is not this light emitted from stars. How do we exclude this starlight?
Answer
Amazingly, cosmic background radiation (CBR) has a perfect blackbody distribution! This CBR is uniform and isotropic in the universe to one part in 100,000 and amazingly flat over large spatial regions that is, large solid angles. One suspects that these large spatial regions, even those in opposite directions in the sky, have always been in communication with each other, to make them so uniform. Of course, smaller regions have their individual characteristic galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and so on.
The most popular interpretation, the standard inflationary model of the universe, requires the universe to originate with the far regions much closer to each other in thermal equilibrium for the observed uniformity to develop, then for a very fast inflation to occur that separated them out of communication reach. Now we see these galaxies, once close together, in opposite directions in the universe and large regions with the same large-scale characteristics in all directions. Their original collective blackbody spectrum at a high temperature now exhibits a low temperature blackbody spectrum because the expansion of the universe has “stretched the wavelengths.”
The stars we see are not in thermal equilibrium as a collective whole. One cannot produce a perfect blackbody spectrum at any temperature by simply using billions of stars that are not in thermal equilibrium as a whole and adding up their radiation intensities in the universe. One cannot obtain a blackbody spectrum from many other hypotheses about the cosmological redshift of light from distant objects, such as the tired-light effect wherein the light loses energy during tranversal of the universe.
One could, however, speculate that the galaxies have never changed their average separations, that there has been no coordinate expansion as stated in the standard inflationary model. The cosmological redshifts would correspond to the redshift produced by an “effective cosmological gravitational potential well” for example, in which the source sits lower in the well than the observer, true for all sources and all observers in the universe. The galaxies would be closer together at all epochs, in communication with each other, and in thermal equilibrium, so the measured uniformity would be expected that is, all directions should look the same.
One consequence would be that one could never see galaxies beyond about 12 billion light-years or so, the actual distance value depending on the average matter/energy density of the vacuum. The redshifts would be interpreted as “effective recession velocities” that reach light speed at this far distance.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|