


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 6-8-2016
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 8-1-2017
|
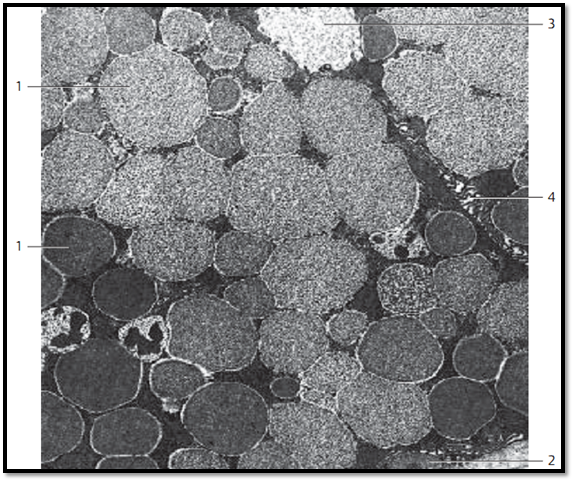
Extraepithelial Glands—Mucous Glands
In light microscopy, the cytoplasm of mucous gland cells appears light. Frequently it is structure d like a honeycomb. The flattened nuclei are locate d in the basal cell space (see Figs. 130, 378). As in serous glands, cells from mucous glands produce many secretory granules, which will finally occupy the entire cell body. Electron microscopy shows different patterns of density for the mucus droplets. These droplets will fuse with each other, especially in the apical cell region, and lose their cell membranes in the process. The mucous droplets are so densely packed that they will supplant other cell organelles and inclusions. Only small cytosol septa are left b e-tween the secretory granules. At the cell periphery is a narrow layer of cytoplasm, which contains the mitochondria, other cell organelles and, in the basal cell region, the flattened nucleus. This figure shows mucus droplets in submandibular gland cells. Neighboring cells interconnect via cell processes. The basal region contains myoepithelial 2 cells. Mucins can be selectively stained using special staining procedures, e.g., Alcian blue staining or the PAS reaction.
1 Secretor y granules
2 Myoepithelial cell
3 Gland lumen
4 Intercellular space, can be recognized as cell border using light microscopy
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 7800
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgar t · New York .



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|