


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية| Presence/absence method ISO 11290-1:1996 Amendment 1:2004 for Listeria monocytogenes in foods |
|
|
|
Read More
Date: 2025-03-03
Date: 18-3-2016
Date: 8-3-2016
|
Presence/absence method ISO 11290-1:1996 Amendment 1:2004 for Listeria monocytogenes in foods
This method of the International Organization for Standardization is applicable to products intended for human consumption or animal feeding.
1. Material required for analysis
Isolation
• Half Fraser Broth
• Fraser Broth
• Agar Listeria Ottaviani & Agosti (ALOA)
• 2nd L. monocytogenes selective isolation medium (chosen by the laboratory)
• Laboratory incubator set to 30 ± 1°C
• Laboratory incubator set to 35 ± 1°C or 37 ± 1°C
• Laboratory incubator set to 25 ± 1°C (optional for motility test)
Confirmation
• Trypticase Soy Agar with 0.6% Yeast Extract (TSA-YE)
• Trypticase Soy Broth with 0.6% Yeast Extract (TSB-YE)
• Motility Test Medium ISO (optional)
• 3% Hydrogen Peroxide (for catalase test)
• Gram Stain Reagents
• Sheep Blood Agar plates
• Purple Broth with 0.5% Xylose tubes
• Purple Broth with 0.5% Rhamnose tubes
• L. monocytogenes culture (e.g. NCTC 11994)
• β-hemolytic Staphylococcus aureus culture (e.g. ATCC 25923 or NCTC 1803) (optional)
• Rhodococcus equii culture (e.g. ATCC 6939 or NCTC 1621) (optional)
• Laboratory incubator set to 25 ± 1°C
• Laboratory incubator set to 37 ± 1°C
2. Procedure
A general flowchart for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in foods using the presence/absence method ISO 11290-1:1996/Amd.1:2004 is shown in Figure 1.
Safety precautions recommended by ISO 11290-1:1996/Amd.1:2004: The tests should be performed in properly equipped laboratories, under the supervision of a skilled microbiologist. Great care should be taken in the disposal of contaminated materials. Female laboratory staff should be made aware of the risk to pregnant women. National legislation may involve more specific demands.
a) Primary enrichment:
Homogenize m grams or m milliliter of the sample with 9m milliliters of Half Fraser Broth. Incubate at 30 ± 1°C/24 ± 2 h.
b) Secondary enrichment: Inoculate 0.1 ml of the Half Fraser Broth (regardless of its color) onto 10 ml tubes of Fraser Broth. Incubate the tubes at 37 ± 1°C/48 ± 2 h (or 35 ± 1°C/48 ± 2 h).
Note b.1) The incubation temperature (35 or 37°C) should be agreed between the parties and recorded in the test report.
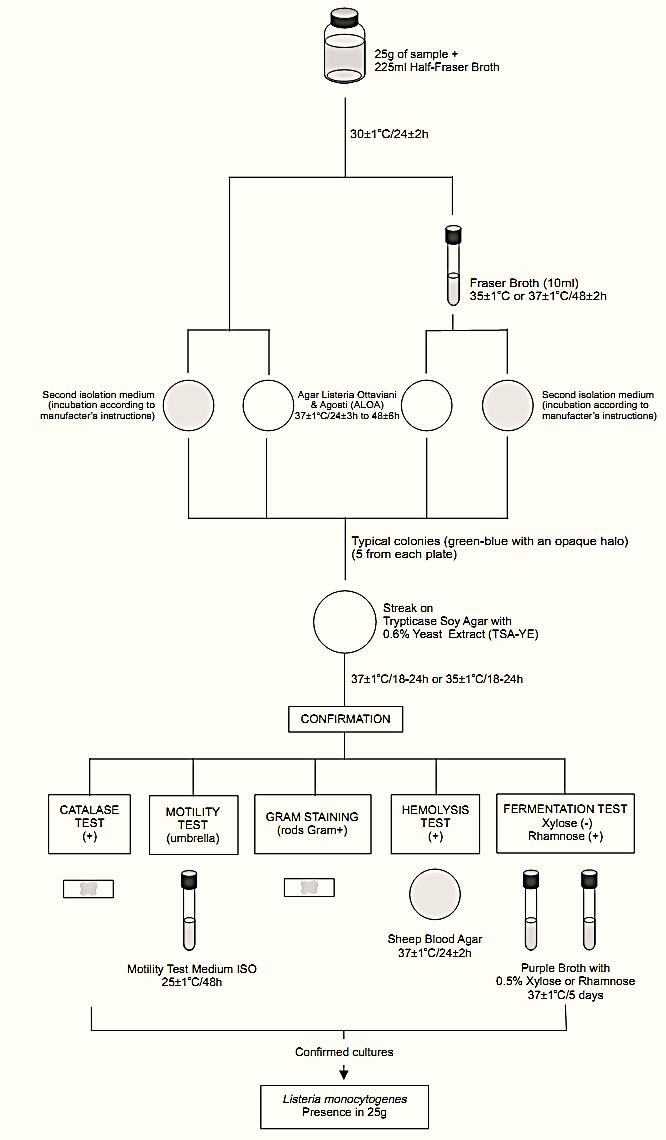
Figure 1 Scheme of analysis for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in foods using the presence/absence method ISO 11290-1:1996/Amd.1:2004.
c) Selective differential plating: From the culture obtained in the primary enrichment (Half Fraser Broth after 24 ± 2 h at 30°C) inoculate the sur-face of the selective isolation medium, Agar Listeria Ottaviani and Agosti (ALOA). Proceed in the same manner with a second L. monocytogenes selective isolation medium, chosen by the laboratory.
From the culture obtained in the secondary enrichment (Fraser Broth after 48 ± 2 h at 37 or 35°C) inoculate the surface of the selective isolation medium, Agar Listeria Ottaviani and Agosti (ALOA). Proceed in the same manner with a second L. monocytogenes selective isolation medium, chosen by the laboratory.
Incubate the ALOA plates at 37 ± 1°C/24+3 h and observe for typical colonies: green-blue surrounded by an opaque halo. If no suspect colonies are evident or if the growth is poor after 24 ± 3 h, re-incubate the plates for an additional 24 h ± 3 h and read again after 48 ± 6 h. Incubate the second isolation medium plates according to the manufacturers’ instructions.
Note c.1) ISO 11290-1:1996/Amd.1:2004 recommends a second isolation medium complementary to ALOA, such as Oxford Agar (OXA) incubated at 35ºC/24–48 h or PALCAM incubated at 35ºC/ 24–48 h or Modified Oxford (MOX) Agar incubated at 35°C/24–48 h or Lithium Chloride Phenylethanol Moxalactam (LPM) Agar supplemented with esculin and Fe3+ incubated at 30°C/24–48 h.
Note c.2) When stressed some strains of L. monocytogenes may show a weak halo or even no halo on ALOA.
Note c.3) The method will not detect strains of L. monocytogenes with slow PIPLC (phosphatidyl inositol phospholipase C) activity (more than four days of incubation are required for these strains).
d) Selection and purification of colonies for confirmation: Select for confirmation five typical colonies from each plate. If there are fewer than five presumptive colonies on a plate, select all. Purify each culture by streaking on a plate of Trypticase Soy Agar with 0.6% Yeast Extract (TSA-YE). Incubate the TSA-YE plates at 37 ± 1°C or 35 ± 1°C for 18–24 h or until growth is satisfactory.
Select one typical well isolated colony from each TSA-YE plate for the confirmatory tests. Typical colonies on TSA exhibit a bluish color and a granular surface when observed with white light at 45° angle. If the suspect colonies on TSA-YE are not isolated, purify by streaking on a fresh TSA-YE plate before starting the tests.
e) Confirmation
References
Silva, N.D .; Taniwaki, M.H. ; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F.A. , Nasdcimento , M.D.D. and Gomes ,R.A.R .(2013) . Microbiological examination methods of food and water a laboratory Manual. Institute of Food Technology – ITAL, Campinas, SP, Brazil .
International Organization for Standardization (2004) ISO 11290-2:1998/Amd.1:2004. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs– Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes – Part 2: Enumeration method. 1st edition:1998, Amendment 1:2004.Geneva, ISO.
International Organization for Standardization (2004) ISO 11290-1:1996/Amd.1:2004. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs – Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes – Part 1: detection method. 1st edition:1996, Amendment 1:2004. Geneva, ISO.



|
|
|
|
دخلت غرفة فنسيت ماذا تريد من داخلها.. خبير يفسر الحالة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ثورة طبية.. ابتكار أصغر جهاز لتنظيم ضربات القلب في العالم
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تدعو جامعة ديالى للمشاركة في حفل التخرج المركزي الخامس
|
|
|