


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 22-2-2020
Date: 19-8-2019
Date: 13-8-2019
|
Consider first the chemical shifts of protons attached to an sp3 carbon, 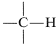 .
.
The degree of shielding of the proton by the carbon valence electrons depends on the character of the substituent atoms and groups present, and particularly on their electron-attracting power, or electronegativity. For a grouping of the type 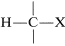 , the shielding will be less as X is more electron withdrawing relative to hydrogen:
, the shielding will be less as X is more electron withdrawing relative to hydrogen:
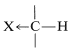 If X is electron-withdrawing, the proton is deshielded.
If X is electron-withdrawing, the proton is deshielded.
For example, the proton chemical shifts of the methyl halides (Table 9-4) show decreasing shielding, hence progressively low-field chemical shifts with increasing halogen electronegativity (F>Cl>Br>I):
Figure 9-28 shows how the shift differences between the CH3− and the −CH2− protons in some CH3CH2X derivatives depend on the electronegativity of X, using the electronegativity defined by L. Pauling. The trend is not wholly linear, but the proton chemical-shift differences become larger the more electronegative X becomes. We can predict with some confidence, therefore, that a molecule such as XCH2CH2Y will have lower-field chemical shifts (larger δ) for XCH2− than for −CH2Y if X is more electronegative than Y:
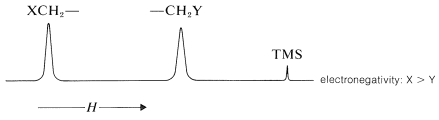
Table 9-4: Typical Proton Chemical-Shift Values (δ) in Dilute CHCl3 Solutions
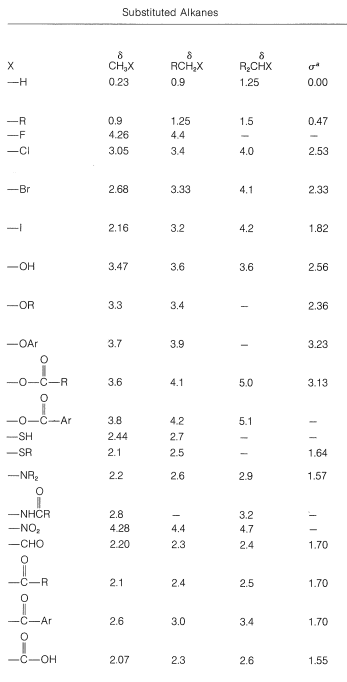
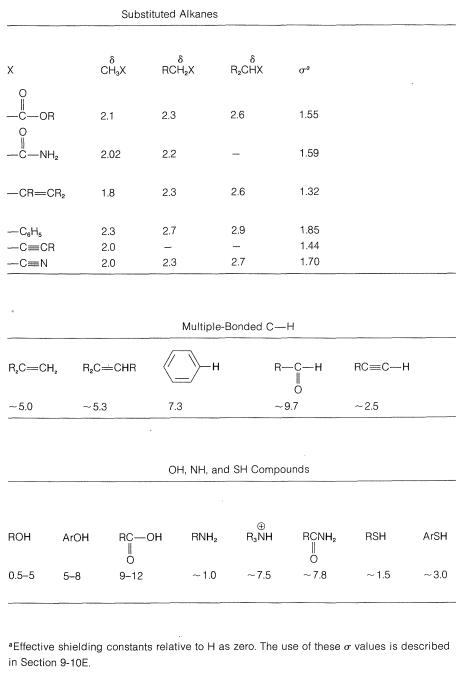
Figure 9-28: Chemical-shift differences between the CH3 and CH2 protons of CH3CH2X derivatives as a function of the Pauling electronegativity of X.
When two electronegative groups, X and Y, are bonded to the same carbon, as in XCH2YXCH2Y, the protons are expected to be less shielded and come into resonance downfield of the methylenes of XCH2CH2Y. There is an approximate relationship (see below) between the shifts of the XCH2Y protons and the effective shielding constants (σ) of X and Y known as Shoolery's rule.
Appropriate values of σσ for use with this equation are given in Table 9-4.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي ينظّم ندوة حوارية حول مفهوم العولمة الرقمية في بابل
|
|
|