


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 24-9-2021
Date: 3-11-2021
Date: 26-11-2021
|
Lipid Absorption by Enterocytes
nonesterified (free) fatty acid (FFA) , free cholesterol, and 2-monoacylglycerol (2-MAG) are the primary products of lipid digestion in the jejunum. These, plus bile salts and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), form mixed micelles (that is, disc-shaped clusters of a mixture of amphipathic lipids that coalesce with their hydrophobic groups on the inside and their hydrophilic groups on the outside). Therefore, mixed micelles are soluble in the aqueous environment of the intestinal lumen (Fig. 1). These particles approach the primary site of lipid absorption,
the brush border membrane of the enterocytes. This microvilli-rich apical membrane is separated from the liquid contents of the intestinal lumen by an unstirred water layer that mixes poorly with the bulk fluid. The hydrophilic surface of the micelles facilitates the transport of the hydrophobic lipids through the unstirred water layer to the brush border membrane where they are absorbed. Bile salts are absorbed in the terminal ileum, with <5% being lost in the feces. [Note: Relative to other dietary lipids, cholesterol is only poorly absorbed by the enterocytes. Drug therapy (for example, with ezetimibe) can further reduce cholesterol absorption in the small intestine.] Because short- and medium-chain FA are water soluble, they do not require the assistance of mixed micelles for absorption by the intestinal mucosa.
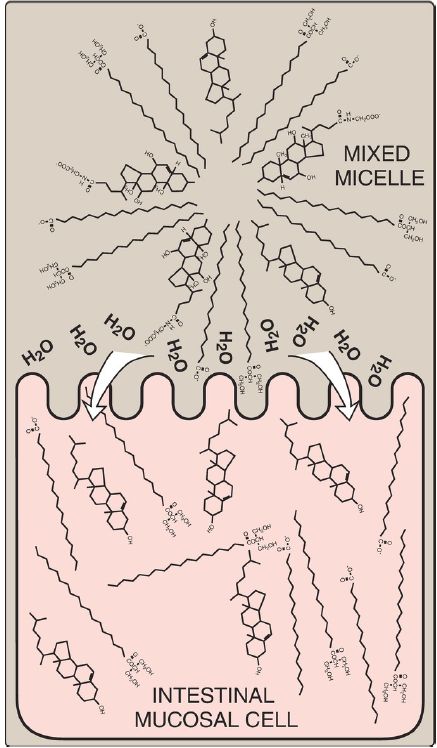
Figure 1: Absorption of lipids contained in a mixed micelle by an intestinal mucosal cell. The micelle itself is not absorbed. [Note: Short- and mediumchain- length fatty acids do not require incorporation into micelles.]



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|