


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 6-2-2017
Date: 4-9-2020
Date: 2-3-2016
|
Solar disc phenomena: Use of a pinhole camera
The simplest means of taking photographs of the Sun is with a pinhole camera. In this system, a tiny hole acts as a lens and the image that it produces can be recorded on film. A very convenient arrangement has the pinhole at one end of a long tube, blackened on its inside, with the body of a single lens reflex camera, without its lens, at the other end.
For the pinhole camera to give reasonable images, the focal ratio must be f/1000 or higher. Thus, a 1 mm hole attached to a 1 m tube is sufficient. Since the Sun subtends about 1/2◦, its image with a 1 m tube is equal to
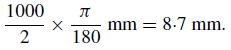
Even with such a focal ratio, the illumination of the Sun’s image is high and a typical exposure of 1/1000th of a second is required using Pan X film. The demand for an extremely high shutter speed may be relaxed by using either a higher focal ratio, filters over the pinhole or a slower film or even a photosensitive photographic paper rather than celluloid film.
A pinhole camera under good conditions is capable of allowing pictures of sunspots to be taken and is useful for recording the shape of the Sun, say at the time of a partial eclipse or when the Sun is just rising or setting. When a celestial object is on the horizon, refraction alters its true altitude by over half a degree. For an extended object such as the Sun, refraction has a differential effect so that the lower limb is more refracted than the upper limb. Thus, when the Sun is close to the horizon, it has an elliptical shape with the lower and upper limbs closer together than the east and west limbs. The distortion is easily seen with the unaided eye at a location where there is an uninterrupted view of the horizon. It may be photographed using a pinhole camera. (An ordinary camera is generally insufficient because of its short focal length.) From measurements of the images, a value for the differential refraction may be determined.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|