


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 13-12-2015
Date: 26-1-2017
Date: 10-2-2017
|
The Central Molecular Zone
Various lines of evidence indicate that a total of 5 × 107 Mּ of relatively dense molecular gas are present in the CMZ, lying predominantly within ±150 pc of the Galactic Center. This represents a much stronger concentration of interstellar matter than anywhere else in the Galaxy. Shows the bulk of the CMZ as revealed by CS emission, which is a probe of moderately dense clouds (nH2 ∼ 104 cm−3). The CMZ has already been described by Huttemeister; here we make a few additional points:
1. Tidal shear. The clouds in the CMZ are easily sheared into tidal streams by the relatively strong differential gravitational forces present in the central few hundred parsecs. A likely example is the ‘Galactic Center Bow’, shown in figure 1.1, from Tsuboi et al (1999). This apparently single molecular structure appears to extend over 300 pc in projection, and probably undergoes most of a complete turn-around the Galactic Center. The stability of clouds against such tidal shear depends on their density. Gusten (1989) derived the following density criterion for cloud stability as a function of galactocentric radius, R:
n ≥ 104 cm−3(75 pc/R)1.8. (1.1)
This condition helps explain why the density of molecular clouds in the CMZ is typically substantially larger than the average molecular cloud density in the Galactic disk. Only the densest molecular clouds in the CMZ, such as Sgr B2, are immune to shear, and thus well localized, and even in those cases, the dense cloud cores are surrounded by a sheared halo.
2. Residence time. Clouds in the CMZ are transient, because their orbital angular momentum is lost by dynamical friction on timescales of several times 108 years (Stark et al 1991). Magnetic torques can cause angular momentum loss on a comparable timescale, given the exceptionally strong magnetic field in the CMZ (Morris 1994, and later). Consequently, the CMZ must be constantly
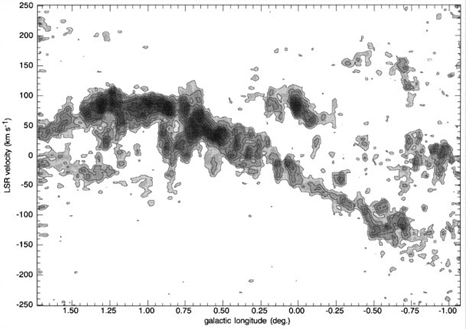
Figure 1.1. CS J = 1-0 position-velocity diagram following the ridge of the ‘Galactic Center bow’ (Tsuboi et al 1999). The ridge is defined by the points [l, b] = [-1.07,−0.20], [-0.75,−0.03], [-0.37, 0.05], [0.50, 0.05], and [1.73,-0.17]. Note how this structure is continuous over 2.5o (375 pc) and 250 km s−1, suggesting that this is a single structure which has been subjected to tidal shearing. It probably wraps at least halfway around the Galactic Center.
replenished, presumably by gas migrating inward from the Galactic disk (Morris and Serabyn 1996; Morris 2001).
What, then, is the fate of the molecular gas which moves inward through the CMZ? Sitting at the bottom of the Galactic potential well, it has only a few possibilities: star formation, ejection in a hot galactic wind, and accretion onto the central black hole. The latter possibility cannot account for any but a tiny fraction of the inflowing gas. The mass of the central black hole and the currently inferred accretion rate onto the black hole are too small by several orders of magnitude for the black hole to be a significant sink for CMZ gas. A thermal galactic wind is a possible contributor (discussed later), but the dominant sink for the CMZ gas is probably star formation, occurring at a rate of a few tenths of a solar mass per year.
3. Asymmetry. The CMZ is quite asymmetric about the Galactic Center, with most of the gas, perhaps 70% of it, lying at positive Galactic longitudes. The thermal dust emission which follows the molecular gas illustrates this asymmetry, as can be seen in the longer-wavelength images. This asymmetry, also present in the velocity field, could be the result of an m = 1 sloshing mode in the gas of the CMZ (discussed by Morris and Serabyn 1996). Notably, the stars do not appear to show a comparable asymmetry, although it would be interesting to seek an asymmetry in the stellar distribution on the scale of the Nuclear Bulge by carefully accounting for extinction. If an m = 1 oscillation is present in the stars and gas at the Galactic Center, corresponding to coupled orbits of the CMZ and Nuclear Bulge about a common center of mass, then the stars and the central black hole would participate in this oscillation, which might manifest itself in terms of their velocities.



|
|
|
|
للتخلص من الإمساك.. فاكهة واحدة لها مفعول سحري
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العلماء ينجحون لأول مرة في إنشاء حبل شوكي بشري وظيفي في المختبر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم العلاقات العامّة ينظّم برنامجاً ثقافياً لوفد من أكاديمية العميد لرعاية المواهب
|
|
|