

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Nomenclature of Heterocycles
المؤلف:
R. R. Gupta, M. Kumar, V. Gupta
المصدر:
Heterocyclic Chemistry I
الجزء والصفحة:
p 4
15-12-2016
2922
Nomenclature of Heterocycles
Systematic Nomenclature System (Hantzsch-Widman System)
This is the most widely used systematic method and is used for naming three- to ten-membered mono cyclic heterocycles of various degree ofunsaturation containing one or more heteroatoms. This nomenclature system specifies the ring size and the nature, type and position(s) of the heteroatom(s). The heteromonocycles are named by using following revised rules of Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature system.
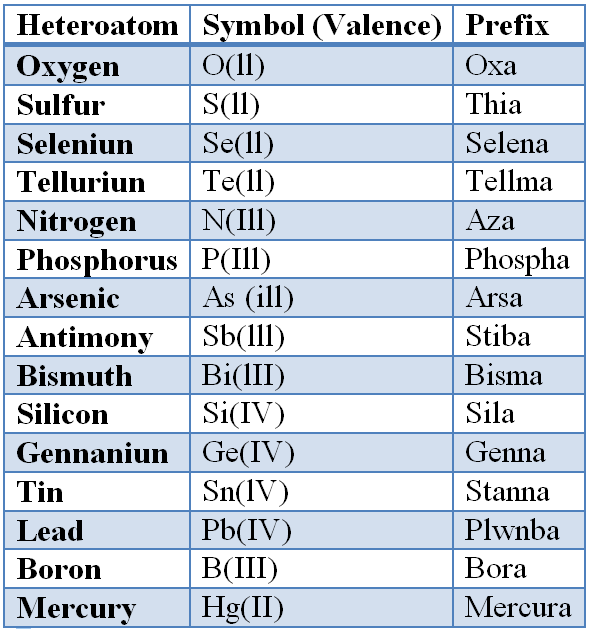
(1) Combination of pretix( es) with stem The heteromonocyclic system is named by combining one or more 'a' prefixes for the heteroatom(s) with a stem indicating the size of the ring. If the stem begins with vowel, the terminal letter 'a' of the 'a' prefix is dropped. Pretixes : The prefixes indicate the heteroatoms present in the heterocyclic systems. The prefixes for different heteroatoms are presented in Table 1 in the preferential order.
Table 1.Prefixes for heteroatoms ('a' prefixes in decreasing order of priority)
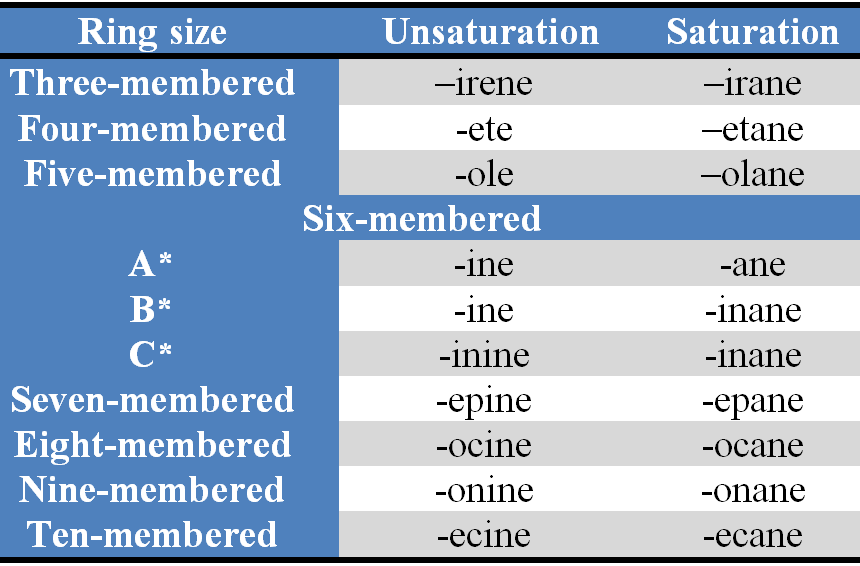
Stems : The stems are used to indicate the size of the ring and the saturation or unsaturation in the heteromonocyclic systems and are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. Stems for tbree- to ten-membered heterocycles
However, the following points should be considered while giving names to the heteromonocycles :
(i) the stem 'irine' is used for three-membered nitrogen-containing unsaturated heteromonocycles.
(n) the stems 'iridine', 'etidine' and 'olidine' are used for nitrogen-containing saturated three-, four- and five-membered heteromonocycles respectively.
(m) the terminal vowel of a numerical prefix is not dropped even when the prefix begins with the same vowel, e.g., cyclotetraazoxane.
(iv) the ending of the Dame depends on the presence or absence of nitrogen.
(v) unsaturated stems are used for the rings with maximum numbers of noncumulative double bonds possilbe, when the heteroatoms have the normal valences given in Table 1.
(vi) saturated stems are used for the rings without double bond(s)
(vii) if the stems are not specified for partialy or completely saturated heteromonocycles, the prefixes 'dihydro-', 'tetrahydro-', etc. should be used.
(viii) the terminal 'e' used in all the stems is optinal (stems without terminal 'e' for unsaturated non-nitrogenous rings with six or more ring members are used in CAS index nomenclature, for example, dioxin, dithiin and oxathiin.
(Ix) the stems 'etine' and 'oline', which were formerly used for nitrogen containing four- and five-membered rings respectively with one double bond have no longer been recommended by IUP AC.
(x) the stems for six-membered rings depend on the least preferred heteroatom in the ring, i.e., the heteroatom immediately preceding the stem. To determine the proper stem for a six-membered ring, the following set containing least preferred heteroatom is selected :
6A * = 0, S, Se, Te, Bi, Hg
6B* = N, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb
6C* = B, P, As, Sb
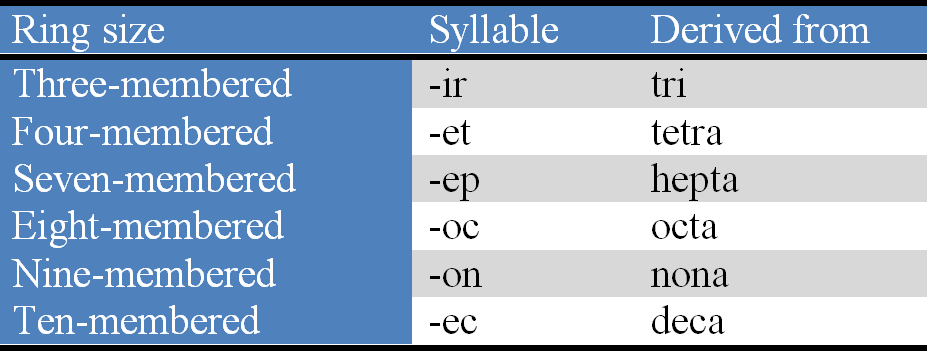
(Xl) the stems (syllables) indicating ring sizes (3, 4, 7, 8, 9 and 10) are considered to be derived from numerical prefixes (Table 3).
(xil) trivial names e.g., pyrrole, pyrazole, imidiazole, pyridine, pyridazine, pyrimidine, etc., permitted for some heteromonocyclic systems by IUPAC should be prefered over the systematic names.
(xiiI) oxine must not be used for pyran because it has been used as a trivial name for quinolin-8-o1.
Table 3. Stems (syllables) for different heterocyclic rings
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















