


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 4-9-2016
Date: 13-7-2016
Date: 10-9-2016
|
Shallow Square Well II
A particle of mass m is confined to move in one dimension by a potential V(x) (see Figure 1.1):
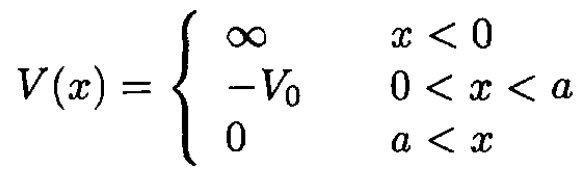 (1)
(1)
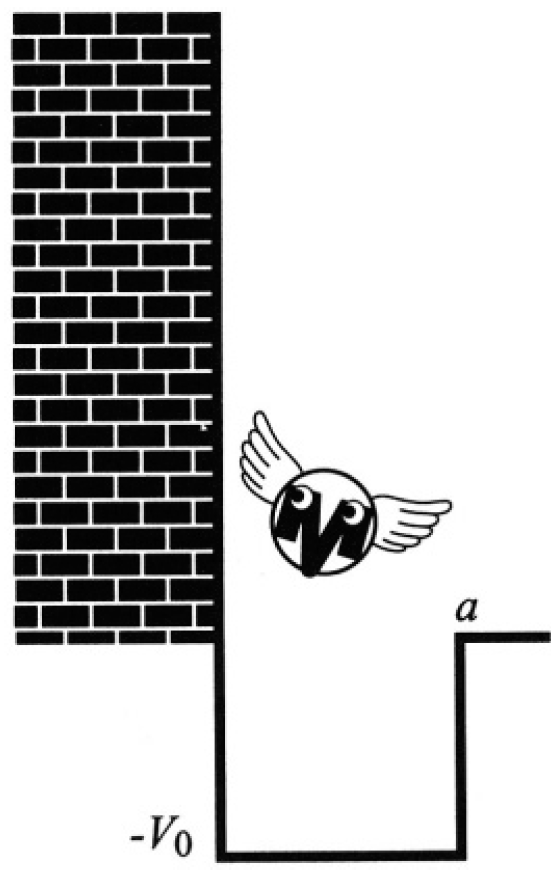
Figure 1.1
a) Derive the equation for the bound state.
b) From the results of part (a), derive an expression for the minimum value of V0 which will have a bound state.
c) Give the expression for the eigenfunction of a state with positive energy E > 0.
d) Show that the results of (c) define a phase shift for the potential, and derive an expression for the phase shift.
SOLUTION
a) For the bound state we can write the eigenvalue as E = -h2α2/2m, where α is the decay constant of the eigenfunction outside the square well. Inside the square well we define a wave vector k by
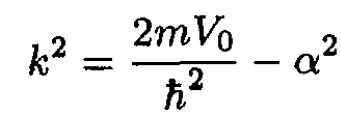 (1)
(1)
The infinite potential at the origin requires that all eigenfunctions vanish at x = 0. So the lowest eigenfunction must have the form
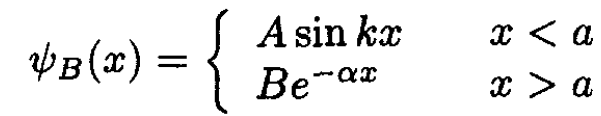 (2)
(2)
At the point x = a, we match the eigenfunctions and their derivatives:
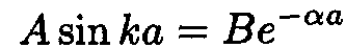 (3)
(3)
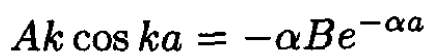 (4)
(4)
We eliminate the constants A and B by dividing these two equations:
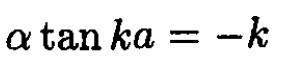 (5)
(5)
Earlier we established the relationship between k and α. So the only unknown variable is α, which is determined by this equation.
b) To find the minimum bound state, we take the limit α → 0 as in the eigenvalue equation. From (1) we see that k goes to a nonzero constant, and the eigenvalue equation only makes sense as α → 0 if tan ka → ∞, which happens at ka → π/2. Using (1) gives π2/4 = k2a2 = 2mV0a2/h2. Thus, we derive the minimum value of V0 for a bound state:
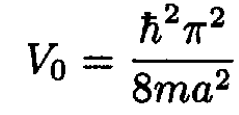 (6)
(6)
c) For a positive energy state set 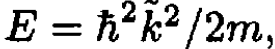 where
where  is the wave vector outside the square well. Inside the square well we again define a wave vector k according to
is the wave vector outside the square well. Inside the square well we again define a wave vector k according to
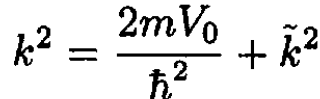 (7)
(7)
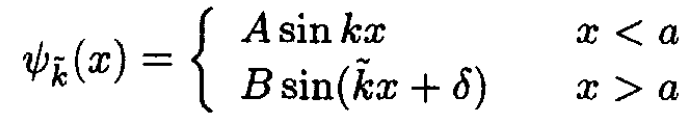 (8)
(8)
Again we have the requirement that the eigenfunction vanish at x = 0. For x > a we have an eigenfunction with two unknown parameters B and δ. Alternatively, we may write it as
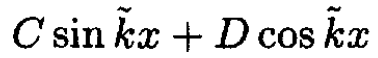 (9)
(9)
in terms of two unknowns C and D. The two forms are equivalent since C = B cos δ, D = B sin δ. We prefer to write it with the phase shift δ. Again we match the two wave functions and their derivatives at x = a:
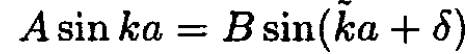 (10)
(10)
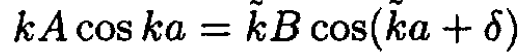 (11)
(11)
Dividing (10) by (11), we obtain
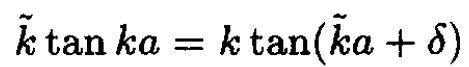 (12)
(12)
Since k is a known function of  the only unknown in this equation is δ, which is determined by this equation.
the only unknown in this equation is δ, which is determined by this equation.
d) From (12) we derive an expression for the phase shift:
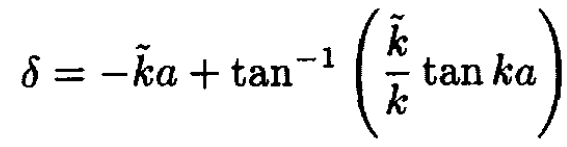 (13)
(13)



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|