


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
أقرأ أيضاً
التاريخ: 18-2-2016
التاريخ: 27-1-2016
التاريخ: 22-11-2020
التاريخ: 13-9-2020
|
In the study of physics, usually the course is divided into a series of subjects, such as mechanics, electricity, optics, etc., and one studies one subject after the other. For example, this course has so far dealt mostly with mechanics. But a strange thing occurs again and again: the equations which appear in different fields of physics, and even in other sciences, are often almost exactly the same, so that many phenomena have analogs in these different fields. To take the simplest example, the propagation of sound waves is in many ways analogous to the propagation of light waves. If we study acoustics in great detail, we discover that much of the work is the same as it would be if we were studying optics in great detail. So, the study of a phenomenon in one field may permit an extension of our knowledge in another field. It is best to realize from the first that such extensions are possible, for otherwise one might not understand the reason for spending a great deal of time and energy on what appears to be only a small part of mechanics.
The harmonic oscillator, which we are about to study, has close analogs in many other fields; although we start with a mechanical example of a weight on a spring, or a pendulum with a small swing, or certain other mechanical devices, we are really studying a certain differential equation. This equation appears again and again in physics and in other sciences, and in fact it is a part of so many phenomena that its close study is well worth our while. Some of the phenomena involving this equation are the oscillations of a mass on a spring; the oscillations of charge flowing back and forth in an electrical circuit; the vibrations of a tuning fork which is generating sound waves; the analogous vibrations of the electrons in an atom, which generate light waves; the equations for the operation of a servosystem, such as a thermostat trying to adjust a temperature; complicated interactions in chemical reactions; the growth of a colony of bacteria in interaction with the food supply and the poisons the bacteria produce; foxes eating rabbits eating grass, and so on; all these phenomena follow equations which are very similar to one another, and this is the reason why we study the mechanical oscillator in such detail. The equations are called linear differential equations with constant coefficients. A linear differential equation with constant coefficients is a differential equation consisting of a sum of several terms, each term being a derivative of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable, and multiplied by some constant. Thus
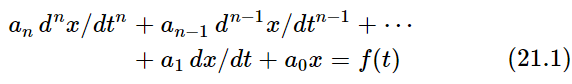
is called a linear differential equation of order n with constant coefficients (each ai is constant).



|
|
|
|
إدارة الغذاء والدواء الأميركية تقرّ عقارا جديدا للألزهايمر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
شراء وقود الطائرات المستدام.. "الدفع" من جيب المسافر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العبّاسيّة: البحوث الّتي نوقشت في أسبوع الإمامة استطاعت أن تثري المشهد الثّقافي
|
|
|