


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 1-11-2021
Date: 3-10-2021
Date: 24-8-2021
|
Cobalamin (Vitamin B12)
Vitamin B12 is required in humans for two essential enzymatic reactions: the remethylation of homocysteine (Hcy) to methionine and the isomerization of methylmalonyl coenzyme A (CoA), which is produced during the degradation of some amino acids (isoleucine, valine, threonine, and methionine) and fatty acids (FA) with odd numbers of carbon atoms (Fig. 1). When cobalamin is deficient, unusual (branched) FA accumulate and become incorporated into cell membranes, including those of the central nervous system (CNS). This may account for some of the neurologic manifestations of vitamin B12 deficiency. [Note: Folic acid (as N5-methyl THF) is also required in the remethylation of Hcy. Therefore, deficiency of B12 or folate results in elevated Hcy levels.]
Figure 28.5 A, B. Reactions requiring coenzyme forms of vitamin B12. CoA =coenzyme A.
A. Structure and coenzyme forms
Cobalamin contains a corrin ring system that resembles the porphyrin ring of heme , but differs in that two of the pyrrole rings are linked directly rather than through a methene bridge. Cobalt is held in the center of the corrin ring by four coordination bonds with the nitrogens of the pyrrole groups. The remaining coordination bonds of the cobalt are with the nitrogen of 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole and with cyanide in commercial preparations of the vitamin in the form of cyanocobalamin (Fig. 2). The physiologic coenzyme forms of cobalamin are 5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin, in which cyanide is replaced with 5′-deoxyadenosine or a methyl group, respectively (see Fig. 2).
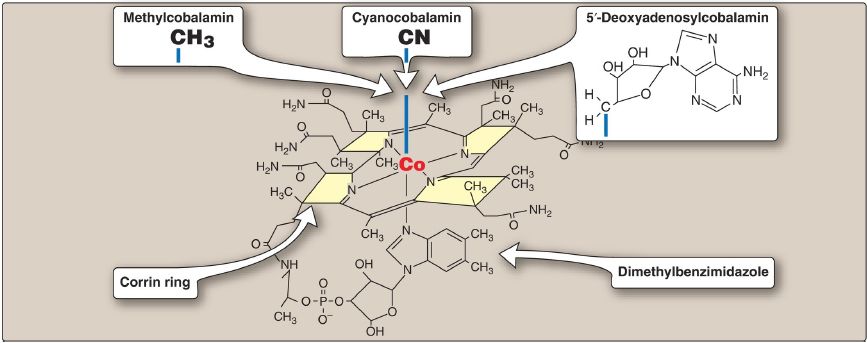
Figure 2: Structure of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and its coenzyme forms (methylcobalamin and 5′-deoxyadenosylcobalamin).
B. Distribution
Vitamin B12 is synthesized only by microorganisms, and it is not present in plants. Animals obtain the vitamin preformed from their intestinal microbiota or by eating foods derived from other animals. Cobalamin is present in appreciable amounts in liver, red meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals.
C. Folate trap hypothesis
The effects of cobalamin deficiency are most pronounced in rapidly dividing cells, such as the erythropoietic tissue of bone marrow and the mucosal cells of the intestine. Such tissues need both the N5,N10-methylene and N10-formyl forms of THF for the synthesis of nucleotides required for DNA replication . However, in vitamin B12 deficiency, the utilization of the N5-methyl form of THF in the B12-dependent methylation of Hcy to methionine is impaired. Because the methylated form cannot be converted directly to other forms of THF, folate is trapped in the N5-methyl form, which accumulates. The levels of the other forms decrease. Thus, cobalamin deficiency leads to a deficiency of the THF forms needed in purine and TMP synthesis, resulting in the symptoms of megaloblastic anemia.



|
|
|
|
للتخلص من الإمساك.. فاكهة واحدة لها مفعول سحري
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العلماء ينجحون لأول مرة في إنشاء حبل شوكي بشري وظيفي في المختبر
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة العميد تحتفي بذكرى ولادة السيدة الزهراء (عليها السلام)
|
|
|