


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 18-2-2021
Date: 1-3-2021
Date: 3-3-2021
|
Cyclotron orbits
If an electron travels with velocity v across a magnetic field B, the Lorentz force −ev × B causes an acceleration perpendicular to the velocity, which produces circular motion. Newton’s second law for the circularly accelerated motion gives f = mev2⊥/r = ev⊥B, so the cyclotron frequency fc = v⊥/2πr is proportional to the field:
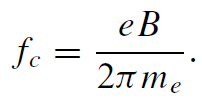 .........(1)
.........(1)
The angular frequency ωc equals 2πfc. Any component of the electron velocity parallel to the magnetic field is uninfluenced by the Lorentz force, so the trajectory is a helix around the field direction. Electrons which follow cyclotron orbits in vacuum radiate energy of frequency fc. The cyclotron frequency is 28 GHz T−1.
The cyclotron radius rc = mev⊥/eB is of order a few micrometres for electrons in metals when B ≈ 1 T. It is less for semiconductors and semimetals, where a smaller electron density leads to a lower Fermi velocity and the effective electron mass m may be less than me.
One example of the use of cyclotron radiation is the domestic microwave oven. Another is the synchrotron, where electrons accelerated to a large multiple γe of their rest energy and constrained to move in curved paths by bending magnets, emit linearly polarized white radiation in a narrow beam of width 1/γe radians. Synchrotron radiation is a valuable tool for probing the electronic structure of solids.



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|