
Lewis Symbols
 المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
 المصدر:
................
المصدر:
................
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 5-7-2020
5-7-2020
 2017
2017
Lewis Symbols
At the beginning of the 20th century, the American chemist G. N. Lewis (1875–1946) devised a system of symbols—now called Lewis electron dot symbols (often shortened to Lewis dot symbols) that can be used for predicting the number of bonds formed by most elements in their compounds. Each Lewis dot symbol consists of the chemical symbol for an element surrounded by dots that represent its valence electrons.
Lewis Dot symbols:
- convenient representation of valence electrons
- allows you to keep track of valence electrons during bond formation
- consists of the chemical symbol for the element plus a dot for each valence electron
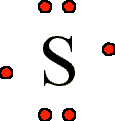
To write an element’s Lewis dot symbol, we place dots representing its valence electrons, one at a time, around the element’s chemical symbol. Up to four dots are placed above, below, to the left, and to the right of the symbol (in any order, as long as elements with four or fewer valence electrons have no more than one dot in each position). The next dots, for elements with more than four valence electrons, are again distributed one at a time, each paired with one of the first four. For example, the electron configuration for atomic sulfur is [Ne]3s23p4, thus there are six valence electrons. Its Lewis symbol would therefore be:
Fluorine, for example, with the electron configuration [He]2s22p5, has seven valence electrons, so its Lewis dot symbol is constructed as follows:

Figure 1. Lewis used the unpaired dots to predict the number of bonds that an element will form in a compound. Consider the symbol for nitrogen in Figure 1. The Lewis dot symbol explains why nitrogen, with three unpaired valence electrons, tends to form compounds in which it shares the unpaired electrons to form three bonds. Boron, which also has three unpaired valence electrons in its Lewis dot symbol, also tends to form compounds with three bonds, whereas carbon, with four unpaired valence electrons in its Lewis dot symbol, tends to share all of its unpaired valence electrons by forming compounds in which it has four bonds.
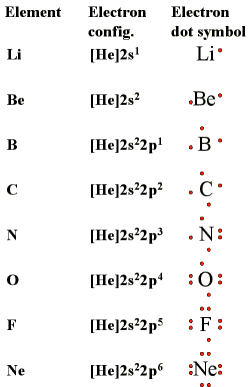
Figure2 : Lewis Dot Symbols for the Elements in Period 2
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


