

 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 2-1-2020
Date: 10-8-2019
Date: 6-1-2020
|
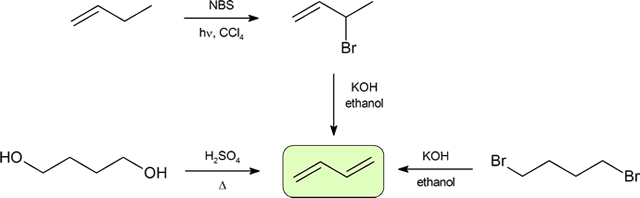
The two most frequent ways to synthesize conjugated dienes are dehydration of alcohols and dehydrohalogenation of organohalides, which were introduced in the preparation of alkenes . The following scheme illustrates some of the routes to preparing a conjugated diene.
The formation of synthetic polymers from dienes such as 1,3-butadiene and isoprene is discussed in Section 14.6. Synthetic polymers are large molecules made up of smaller repeating units. You are probably somewhat familiar with a number of these polymers; for example, polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene and poly(vinyl chloride).
As the hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene releases less than the predicted amount of energy, the energy content of 1,3-butadiene must be lower than we might have expected. In other words, 1,3-butadiene is more stable than its formula suggests.

Figure 1.1 : Energy diagram for the hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene (not to scale).
Conjugated dienes are more stable than non conjugated dienes (both isolated and cumulated) due to factors such as delocalization of charge through resonance and hybridization energy. This can also explain why allylic radicals are much more stable than secondary or even tertiary carbocations. This is all due to the positioning of the pi orbitals and ability for overlap to occur to strengthen the single bond between the two double bonds.
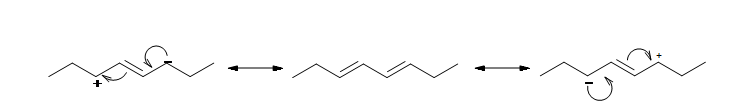
The resonance structure shown below gives a good understanding of how the charge is delocalized across the four carbons in this conjugated diene. This delocalization of charges stablizes the conjugated diene:
Along with resonance, hybridization energy effect the stability of the compound. For example in 1,3-butadiene the carbons with the single bond are sp2 hybridized unlike in nonconjugated dienes where the carbons with single bonds are sp3 hybridized. This difference in hybridization shows that the conjugated dienes have more 's' character and draw in more of the pi electrons, thus making the single bond stronger and shorter than an ordinary alkane C-C bond (1.54Å).

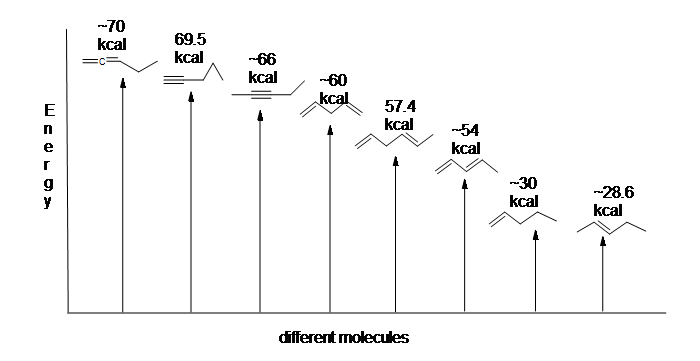
Another useful resource to consider are the heats of hydrogenation of different arrangements of double bonds. Since the higher the heat of hydrogenation the less stable the compound, it is shown below that conjugated dienes (~54 kcal) have a lower heat of hydrogenation than their isolated (~60 kcal) and cumulated diene (~70 kcal) counterparts.
Here is an energy diagram comparing different types of bonds with their heats of hydrogenation to show relative stability of each molecule:
The stabilization of dienes by conjugation is less dramatic than the aromatic stabilization of benzene. Nevertheless, similar resonance and molecular orbital descriptions of conjugation may be written.



|
|
|
|
تفوقت في الاختبار على الجميع.. فاكهة "خارقة" في عالم التغذية
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أمين عام أوبك: النفط الخام والغاز الطبيعي "هبة من الله"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
قسم شؤون المعارف ينظم دورة عن آليات عمل الفهارس الفنية للموسوعات والكتب لملاكاته
|
|
|