

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The SN2 mechanism
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
31-7-2019
1465
The SN2 mechanism
There are two mechanistic models for how an alkyl halide can undergo nucleophilic substitution. In the first picture, the reaction takes place in a single step, and bond-forming and bond-breaking occur simultaneously. (In all figures in this section, 'X' indicates a halogen substituent).
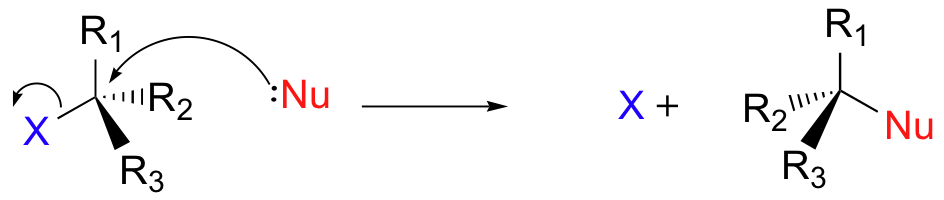
This is called an 'SN2' mechanism. In the term SN2, S stands for 'substitution', the subscript N stands for 'nucleophilic', and the number 2 refers to the fact that this is a bimolecular reaction: the overall rate depends on a step in which two separate molecules (the nucleophile and the electrophile) collide. A potential energy diagram for this reaction shows the transition state (TS) as the highest point on the pathway from reactants to products.

If you look carefully at the progress of the SN2 reaction, you will realize something very important about the outcome. The nucleophile, being an electron-rich species, must attack the electrophilic carbon from the back side relative to the location of the leaving group. Approach from the front side simply doesn't work: the leaving group - which is also an electron-rich group - blocks the way.

The result of this backside attack is that the stereochemical configuration at the central carbon inverts as the reaction proceeds. In a sense, the molecule is turned inside out. At the transition state, the electrophilic carbon and the three 'R' substituents all lie on the same plane.

What this means is that SN2 reactions whether enzyme catalyzed or not, are inherently stereoselective: when the substitution takes place at a stereocenter, we can confidently predict the stereochemical configuration of the product. Below is an animation illustrating the principles we have just learned, showing the SN2 reaction between hydroxide ion and methyl iodide. Notice how backside attack by the hydroxide nucleophile results in inversion at the tetrahedral carbon electrophile.
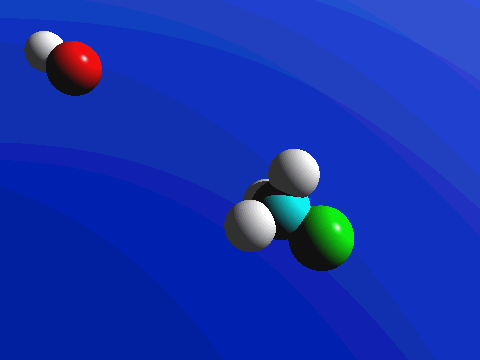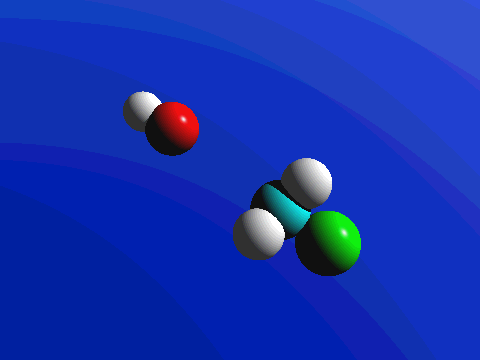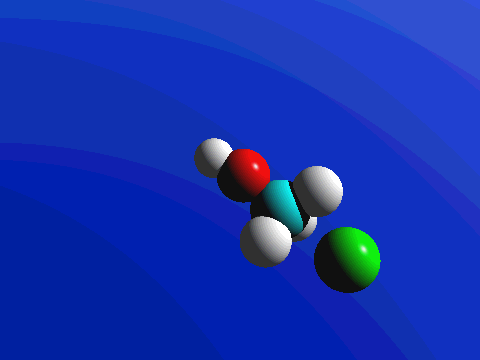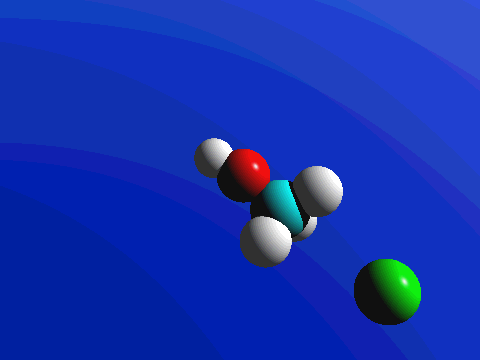
Exercise
Predict the structure of the product in this SN2 reaction. Be sure to specify stereochemistry.
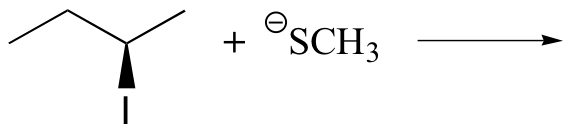
We will be contrasting about two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions. One type is referred to as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1), whereby the rate determining step is unimolecular and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2), whereby the rate determining step is bimolecular. We will begin our discussion with SN2 reactions, and discuss SN1 reactions elsewhere.
 الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















