

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 332
24-9-2017
3340
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used thermoplastics. It can be extruded into sheets and film and blow molded into bottles. It is used in many common items such as garden hoses, shower curtains, irrigation pipes, and paint formulations. PVC can be prepolymerized in bulk to approximately 7–8% conversion. It is then transferred to an autoclave where the particles are polymerized to a solid powder. Most vinyl chloride, however, is polymerized in suspension reactors made of stainless steel or glass-lined. The peroxide used to initiate the reaction is dispersed in about twice its weight of water containing 0.01–1% of a stabilizer such as polyvinyl alcohol.l8 In the European Vinyls Corp. process (Figure 1.1), vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) is dispersed in water and then charged with the additives to the reactor.
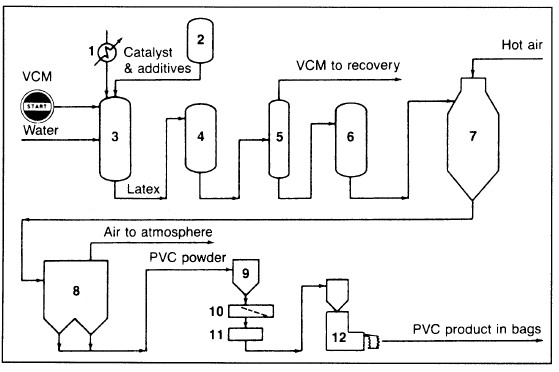
Figure 1.1. The European Vinyls Corp. process for producing polyvinyl chloride using suspension polymerization: (1) reactor, (2) blow-down vessels (to separate unreacted monomer), (3) stripping column, (4) reacted monomer recovery, (5) slurry centrifuge, (6) slurry drier.
It is a stirred jacketed type ranging in size between 20–105m3. The temperature is maintained between 53–70°C to obtain a polymer of a particular molecular weight. The heat of the reaction is controlled by cooling water in the jacket and by additional reflux condensers for large reactors. Conversion could be controlled between 85–95% as required by the polymer grade. At the end of the reaction, the PVC and water slurry are channelled to a blowdown vessel, from which part of unreacted monomer is recovered. The rest of the VCM is stripped, and the slurry is centrifuged to separate the polymer from both water and the initiator.
Polyvinyl chloride can also be produced in emulsion. Water is used as the emulsion medium. The particle size of the polymer is controlled using the proper conditions and emulsifier. Polymers produced by free radical initiators are highly branched with low crystallinity.
Vinyl chloride can be copolymerized with many other monomers to improve its properties. Examples of monomers used commercially are vinyl acetate, propylene, ethylene, and vinylidine chloride. The copolymer with ethylene or propylene (Tg = 80°C), which is rigid, is used for blow molding objects. Copolymers with 6–20% vinyl acetate (Tg = 50–80°C ) are used for coatings.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء البوليمرات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















