
Maleic anhydride
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p242
الجزء والصفحة:
p242
 3-9-2017
3-9-2017
 1657
1657
Maleic anhydride
Maleic anhydride, a solid compound that melts at 53°C,is soluble in water, alcohol, and acetone, but insoluble in hydrocarbon solvents. The production of maleic anhydride from n-butenes is a catalyzed reaction occurring at approximately 400–440°C and 2–4 atmospheres. A special catalyst, constituted of an oxide mixture of molybdenum, vanadium, and phosphorous, may be used. Approximately 45% yield of maleic anhydride could be obtained from this route:

Other routes to maleic anhydride are the oxidation of n-butane, a major source for this compound and the oxidation of benzene.
Maleic anhydride is important as a chemical because it polymerizewith other monomers while retaining the double bond, as in unsaturated polyester resins. These resins, which represent the largest end use of maleic anhydride, are employed primarily in fiber-reinforced plastics for the construction, marine, and transportation industries. Maleic anhydride can also modify drying oils such as linseed and sunflower.
As an intermediate, maleic anhydride is used to produce malathion, an important insecticide, and maleic hydrazide, a plant growth regulator:
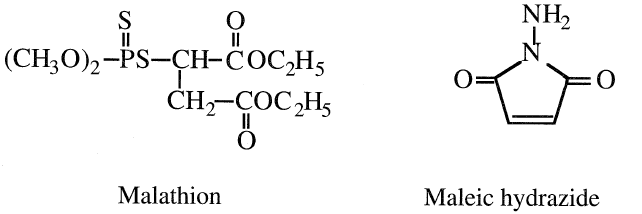
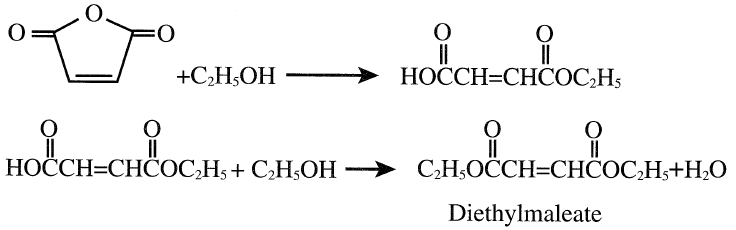
Maleic anhydride is also a precursor for 1,4-butanediol through an esterification route followed by hydrogenation. In this process, excess ethyl alcohol esterifies maleic anhydride to monoethyl maleate. In a second step, the monoester catalytically esterifies to the diester. Excess ethanol and water are then removed by distillation. The ethanol-water mixture is distilled to recover ethanol, which is recycled:
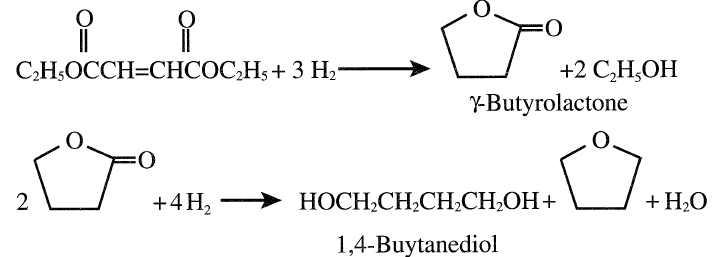
Hydrogenation of diethylmaleate in the vapor phase over a nonprecious metal catalyst produces diethyl succinate. Successive hydrogenation produces γ-butyrolactone, butanediol, and tetrahydrofuran.
Selectivity to the coproducts is high, but the ratios of the coproducts may be controlled with appropriate reactor operating conditions. Figure 1.1 is a block diagram for the butane diol process. 1,4-Butanediol from butadiene is discussed later in this chapter.
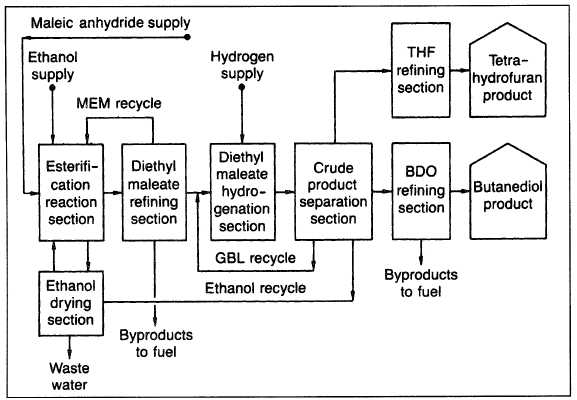
Figure 1.1. A block diagram for producing 1,4-butanediol from maleic anhydride.
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


