

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
HYDRATION OF PROPYLENE (Isopropanol [CH3CHOHCH3])
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
الجزء والصفحة:
p 227
31-8-2017
7710
HYDRATION OF PROPYLENE (Isopropanol [CH3CHOHCH3])
Isopropanol (2-propanol) is an important alcohol of great synthetic utility. It is the second-largest volume alcohol after methanol (1998 U.S. production was approximately 1.5 billion pounds) and it was the 49th ranked chemical. Isopropanol under the name “isopropyl alcohol” was the first industrial chemical synthesized from a petroleum-derived olefin (1920).
The production of isopropanol from propylene occurs by either a direct hydration reaction (the newer method) or by the older sulfation reaction followed by hydrolysis. In the direct hydration method, the reaction could be effected either in a liquid or in a vapor-phase process. The slightly exothermic reaction evolves 51.5 KJ/mol.
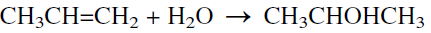
In the liquid-phase process, high pressures in the range of 80–100 atmospheres are used. A sulfonated polystyrene cation exchange resin is the catalyst commonly used at about 150°C. An isopropanol yield of 93.5% can be realized at 75% propylene conversion. The only important byproduct is diisopropyl ether (about 5%). Figure 1.1 is a flow diagram of the propylene hydration process.
Gas phase hydration, on the other hand, is carried out at temperatures above 200°C and approximately 25 atmospheres. The ICI process employs WO3 on a silica carrier as catalyst.
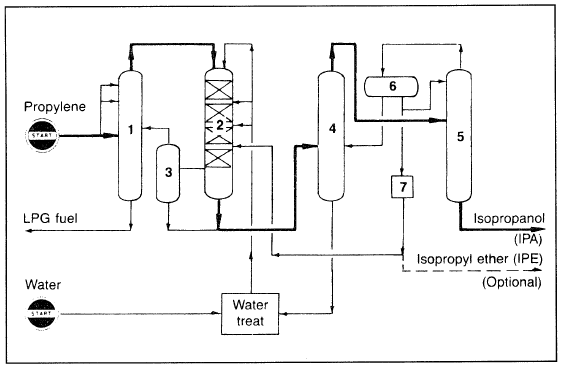
Figure 1.1. A flow diagram for the hydration of propylene to isopropanol:16 (1) propylene recovery column, (2) reactor, (3) residual gas separation column, (4) aqueous - isopropanol azeotropic distillation column, (5) drying column, (6) isopropyl ether separator, (7) isopropyl ether extraction.
Older processes still use the sulfation route. The process is similar to that used for ethylene in the presence of H2SO4, but the selectivity is a little lower than the modern vapor-phase processes. The reaction conditions are milder than those used for ethylene. This manifests the greater ease with which an isopropyl carbocation (a secondary carbonium ion) is formed than a primary ethyl carbonium ion:
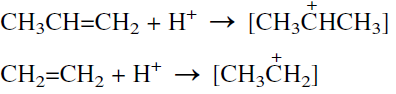
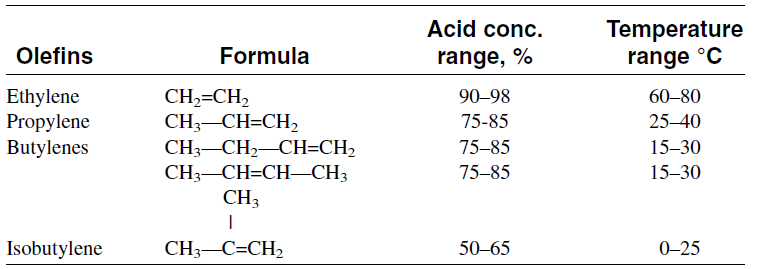
Table 1.1 compares sulfuric acid concentrations and the temperatures used for the sulfation of different light olefins
Table 1.1 : Acid concentration and temperatures used for the sulfation of various olefins
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















