
Ethylene oxide Production
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 190
الجزء والصفحة:
p 190
 22-8-2017
22-8-2017
 1927
1927
Ethylene oxide Production
The main route to ethylene oxide is oxygen or air oxidation of ethylene over a silver catalyst. The reaction is exothermic; heat control is important:
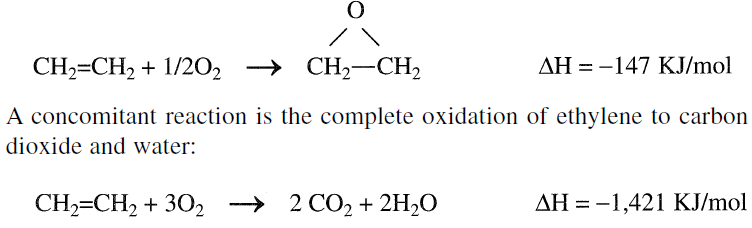
This reaction is highly exothermic; the excessive temperature increase reduces ethylene oxide yield and causes catalyst deterioration. Overoxidation can be minimized by using modifiers such as organic chlorides. It seems that silver is a unique epoxidation catalyst for ethylene. All other catalysts are relatively ineffective, and the reaction to ethylene is limited among lower olefins. Propylene and butylenes do not form epoxides through this route.
Using oxygen as the oxidant versus air is currently favored because it is more economical. In the process (Figure 1.1), compressed oxygen, ethylene, and recycled gas are fed to a multitubular reactor. The temperature of oxidation is controlled by boiling water in the shell side of the reactor.
. 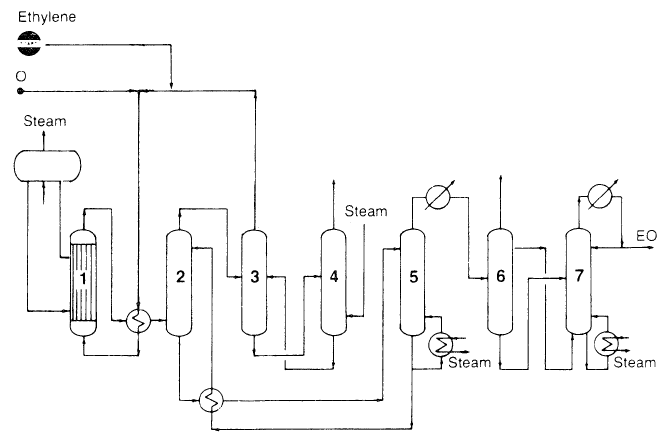
Figure 1.1. The Scientific Design Co. Ethylene Oxide process:5 (1) reactor, (2) scrubber, (3,4) CO2 removal, (5) stripper, (6,7) fractionators.
Effluent gases are cooled and passed to the scrubber where ethylene oxide is absorbed as a dilute aqueous solution. Unreacted gases are recycled. Epoxidation reaction occurs at approximately 200–300°C with a short residence time of one second. A selectivity of 70–75% can be reached for the oxygen based process. Selectivity is the ratio of moles of ethylene oxide produced per mole of ethylene reacted. Ethylene oxide selectivity can be improved when the reaction temperature is lowered and the conversion of ethylene is decreased (higher recycle of unreacted gases).
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


