
Maleic Anhydride
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 176
الجزء والصفحة:
p 176
 21-8-2017
21-8-2017
 2449
2449
Maleic Anhydride
Catalytic oxidation of n-butane at 490° over a cerium chloride, Co-Mo oxide catalyst produces maleic anyhydride:

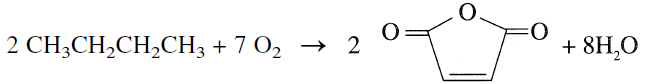
Other catalyst systems such as iron V2O5-P2O5 over silica alumina are used for the oxidation. In the Monsanto process (Figure 1.1), n-butane and air are fed to a multitube fixed-bed reactor, which is cooled with molten salt.
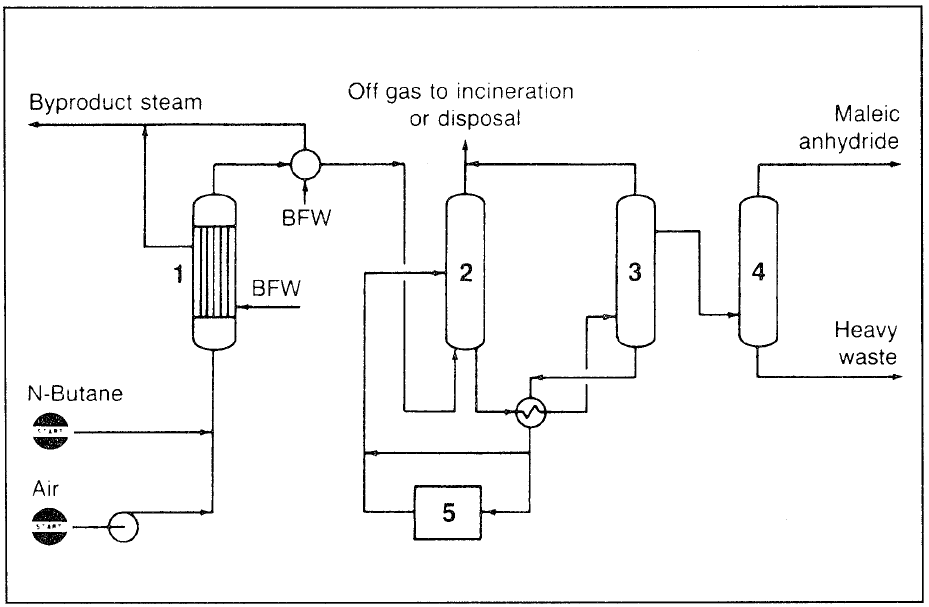
Figure 1.1. The Monsanto process for producing maleic anhydride from butane: (1) reactor, (2) absorber (3) stripper, (4) fractionator, (5) solvent purification.
The catalyst used is a proprietary modified vanadium oxide. The exit gas stream is cooled, and crude maleic anhydride is absorbed then recovered from the solvent in the stripper. Maleic anhydride is further purified using a proprietary solvent purification system.
A new process for the partial oxidation of n-butane to maleic anhydride was developed by DuPont. The important feature of this process is the use of a circulating fluidized bed-reactor. Solids flux in the rizerreactor is high and the superficial gas velocities are also high, which encounters short residence times usually in seconds. The developed catalyst for this process is based on vanadium phosphorous oxides (VO)2P2O7 type, which provides the oxygen needed for oxidation. The selective oxidation of n-butane to maleic anhydride involves a redox mechanism where the removal of eight hydrogen atoms as water and the insertion of three oxygen atoms into the butane molecule occurs. The reaction temperature is approximately 500°C. Subsequent hydrogenation of maleic anhydride produces tetrahydrofuran. Figure 1.2 shows the DuPont butane to maleic anhydride process. Oxidation of n-butane to maleic anhydride is becoming a major source for this important chemical.
The principal use of maleic anhydride is in the synthesis of unsaturated polyester resins. These resins are used to fabricate glass-fiber reinforced materials. Other uses include fumaric acid, alkyd resins, and pesticides. Maleic acid esters are important plasticizers and lubricants.


Figure 1.2. The DuPont butane to maleic anhydride process
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


