
NATURAL GAS
 المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
المؤلف:
sami matar & Lewis. F. Hatch
 المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
المصدر:
Chemistry of PETROCHEMICAL PROCESSES
 الجزء والصفحة:
2th p .1
الجزء والصفحة:
2th p .1
 23-11-2015
23-11-2015
 2546
2546
NATURAL GAS
(Non-associated and Associated Natural Gases)
Natural gas is a naturally occurring mixture of light hydrocarbons accompanied by some non-hydrocarbon compounds. Non-associated natural gas is found in reservoirs containing no oil (dry wells).
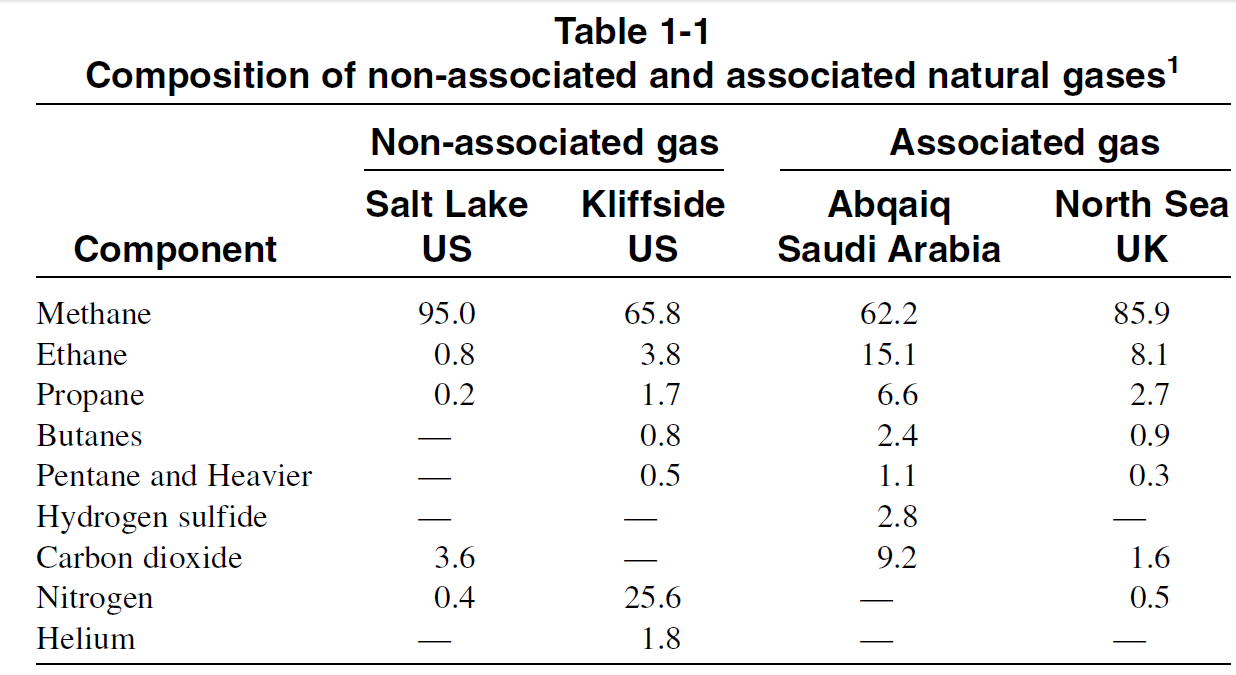
Associated gas, on the other hand, is present in contact with and/or dissolved in crude oil and is coproduced with it. The principal component of mostnatural gases is methane. Higher molecular weight paraffinic hydrocarbons (C2-C7) are usually present in smaller amounts with the natural gas mixture, and their ratios vary considerably from one gas field to another. Non-associated gas normally contains a higher methane ratio than associated gas, while the latter contains a higher ratio of heavier hydrocarbons.
Table 1-1 shows the analyses of some selected non-associated and associated gases.1 In our discussion, both non-associated and associated gases will be referred to as natural gas. However, important differences will be noted. The non-hydrocarbon constituents in natural gas vary appreciably from one gas field to another. Some of these compounds are weak acids, such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide. Others are inert, such as nitrogen, helium and argon. Some natural gas reservoirs contain enough helium for commercial production.
Higher molecular weight hydrocarbons present in natural gases are important fuels as well as chemical feedstock's and are normally recovered as natural gas liquids. For example, ethane may be separated for use as a feedstock for steam cracking for the production of ethylene. Propane and butane are recovered from natural gas and sold as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). Before natural gas is used it must be processed or treated to remove the impurities and to recover the heavier hydrocarbons (heavier than methane). The 1998 U.S. gas consumption was approximately 22.5 trillion ft3 .
 الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
الاكثر قراءة في البترو كيمياويات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


