
Folic Acid: Nutritional anemias
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 8-12-2021
8-12-2021
 1846
1846
Folic Acid: Nutritional anemias
Anemia is a condition in which the blood has a lower than normal concentration of hemoglobin, which results in a reduced ability to transport oxygen (O2). Nutritional anemias (that is, those caused by inadequate intake of one or more essential nutrients) can be classified according to the size of the red blood cells (RBC), or mean corpuscular volume (MCV), observed in the blood (Fig. 2). Microcytic anemia (MCV below normal), caused by lack of iron, is the most common form of nutritional anemia. The second major category of nutritional anemia, macrocytic (MCV above normal), results from a deficiency in folic acid or vitamin B12. [Note: These macrocytic anemias are commonly called megaloblastic because a deficiency of either vitamin (or both) causes accumulation of large, immature RBC precursors, known as megaloblasts, in the bone marrow and the blood (Fig. 3). Hypersegmented neutrophils are also seen.]

Figure 1: Production and use of tetrahydrofolate. NADP(H) = nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
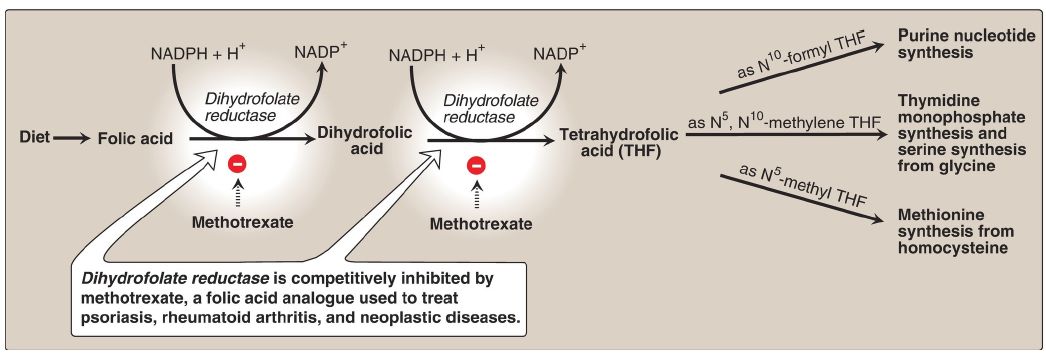
Figure 2: Classification of nutritional anemias by red cell size. The normal mean corpuscular volume (MCV) for people older than age 18 years is 80–100 μm3. [Note: Microcytic anemia is also seen with heavy metal (for example, lead) poisoning.]
1. Folate and anemia: Inadequate serum levels of folate can be caused by increased demand (for example, pregnancy and lactation), poor absorption caused by pathology of the small intestine, alcoholism, or treatment with drugs (for example, methotrexate) that are dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (see Fig. 28.1). A folate-free diet can cause a deficiency within a few weeks. A primary result of folic acid deficiency is megaloblastic anemia (see Fig. 3), caused by diminished synthesis of purine nucleotides and TMP, which leads to an inability of cells (including RBC precursors) to make DNA and, therefore, an inability to divide.

Figure 3: Bone marrow histology in normal (A) and folate-deficient (B) individuals.
2. Folate and neural tube defects: Spina bifida and anencephaly, the most common neural tube defects (NTD), affect ~3,000 pregnancies in the United States annually. Folic acid supplementation before conception and during the first trimester has been shown to significantly reduce NTD. Therefore, all women of childbearing age are advised to consume 0.4 mg/day (400 μg/day) of folic acid to reduce the risk of having a pregnancy affected by NTD and ten times that amount if a previous pregnancy was affected. Adequate folate nutrition must occur at the time of conception because critical folate-dependent development occurs in the first weeks of fetal life, at a time when many women are not yet aware of their pregnancy. In 1998, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration authorized the addition of folic acid to wheat flour and enriched grain products, resulting in a dietary supplementation of ~0.1 mg/day. This supplementation allows ~50% of all reproductive-aged women to receive 0.4 mg of folate from all sources.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


