

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Branched-chain amino acid degradation
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
9-11-2021
1724
Branched-chain amino acid degradation
The BCAA isoleucine, leucine, and valine are essential amino acids. In contrast to other amino acids, they are catabolized primarily by the peripheral tissues (particularly muscle), rather than by the liver. Because these three amino acids have a similar route of degradation, it is convenient to describe them as a group (see Fig. 1).
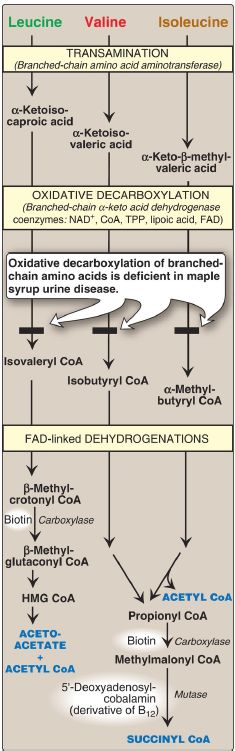
Figure 1: Degradation of leucine, valine, and isoleucine. [Note: β- Methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase is one of four biotin-requiring carboxylases discussed in this book. The other three are pyruvate carboxylase, acetyl CoA carboxylase, and propionyl CoA carboxylase.] TPP = thiamine pyrophosphate; FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide; CoA = coenzyme A; NAD = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; HMG = hydroxymethylglutarate.
1. Transamination: Transfer of the amino groups of all three BCAA to α-ketoglutarate is catalyzed by a single, vitamin B6–requiring enzyme, branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase, that is expressed primarily in skeletal muscle.
2. Oxidative decarboxylation: Removal of the carboxyl group of the α-keto acids derived from leucine, valine, and isoleucine is catalyzed by a single multienzyme complex, branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase (BCKD) complex. This complex uses thiamine pyrophosphate, lipoic acid, oxidized flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), NAD+, and CoA as its coenzymes and produces NADH. [Note: This reaction is similar to the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex and α-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA by the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex . The dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (Enzyme 3, or E3) component is identical in all three complexes.]
3. Dehydrogenations: Oxidation of the products formed in the BCKD reaction produces α-β-unsaturated acyl CoA derivatives and FADH2. These reactions are analogous to the FAD-linked dehydrogenation in the β-oxidation of fatty acids . [Note: Deficiency in the dehydrogenase specific for isovaleryl CoA causes neurologic problems and is associated with a “sweaty feet” odor in body fluids.]
4. End products: The catabolism of isoleucine ultimately yields acetyl Co and succinyl CoA, rendering it both ketogenic and glucogenic. Valine yields succinyl CoA and is glucogenic. Leucine is ketogenic, being metabolized to acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. In addition, NADH and FADH2 are produced in the decarboxylation and dehydrogenation
reactions, respectively. [Note: BCAA catabolism also results in glutamine and alanine being synthesized and sent out into the blood from muscle .]
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















