
Amino Acids that form Succinyl CoA: Methionine
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 7-11-2021
7-11-2021
 2790
2790
Amino Acids that form Succinyl CoA: Methionine
Methionine is one of four amino acids that form succinyl CoA. This sulfurcontaining amino acid deserves special attention because it is converted to S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), the major methyl group donor in one-carbon metabolism (Fig. 1). Methionine is also the source of homocysteine (Hcy), a metabolite associated with atherosclerotic vascular disease and thrombosis .
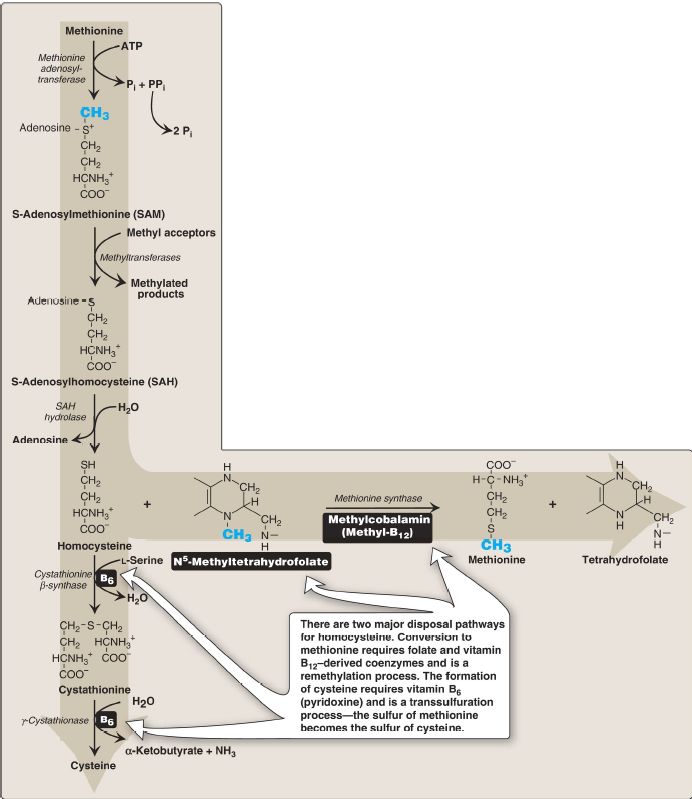
Figure 1: Degradation and resynthesis of methionine. [Note: The resynthesis of methionine from homocysteine is the only reaction in which tetrahydrofolate both carries and donates a methyl (−CH3) group. In all other reactions, SAM is the methyl group carrier and donor.] PPi = pyrophosphate; Pi = inorganic phosphate; NH3 = ammonia.
1. S-Adenosylmethionine synthesis: Methionine condenses with ATP, forming SAM, a high-energy compound that is unusual in that it contains no phosphate. The formation of SAM is driven by hydrolysis of all three phosphate bonds in ATP (see Fig. 1).
2. Activated methyl group: The methyl group attached to the sulfur in SAM is activated and can be transferred by methyltransferases to a variety of acceptors such as norepinephrine in the synthesis of epinephrine. The methyl group is usually transferred to nitrogen or oxygen atoms (as with epinephrine synthesis and degradation, respectively) and sometimes to carbon atoms (as with cytosine). The reaction product, Sadenosylhomocysteine (SAH), is a simple thioether, analogous to methionine. The resulting loss of free energy makes methyl transfer essentially irreversible.
3. S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolysis: After donation of the methyl group, SAH is hydrolyzed to Hcy and adenosine. Hcy has two fates. If there is a deficiency of methionine, Hcy may be remethylated to methionine (see Fig. 1). If methionine stores are adequate, Hcy may enter the transsulfuration pathway, where it is converted to cysteine. a. Methionine resynthesis: Hcy accepts a methyl group from N5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methyl-THF) in a reaction requiring methylcobalamin, a coenzyme derived from vitamin B12). [Note: The methyl group is transferred by methionine synthase from the B12 derivative to Hcy, regenerating methionine. Cobalamin is remethylated from N5-methyl-THF.]
b. Cysteine synthesis: Hcy condenses with serine, forming cystathionine, which is hydrolyzed to α-ketobutyrate and cysteine (see Fig. 1). This vitamin B6–requiring sequence has the net effect of converting serine to cysteine and Hcy to α-ketobutyrate, which is oxidatively decarboxylated to form propionyl CoA. Propionyl CoA is converted to succinyl CoA . Because Hcy is synthesized from the essential amino acid methionine, cysteine is not an essential amino acid as long as sufficient methionine is available.
4. Relationship of homocysteine to vascular disease: Elevations in plasma Hcy levels promote oxidative damage, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction and are an independent risk factor for occlusive vascular diseases such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and stroke (Fig. 2).
Mild elevations (hyperhomocysteinemia) are seen in ~7% of the population. Epidemiologic studies have shown that plasma Hcy levels are inversely related to plasma levels of folate, B12, and B6, the three vitamins involved in the conversion of Hcy to methionine and cysteine.
Supplementation with these vitamins has been shown to reduce circulating levels of Hcy. However, in patients with established CVD, vitamin therapy does not decrease cardiovascular events or death. This raises the question as to whether Hcy is a cause of the vascular damage or merely a marker of such damage. [Note: Large elevations in plasma Hcy as a result of rare deficiencies in cystathionine β-synthase of the transsulfuration pathway are seen in patients with classic homocystinuria (resulting from severe hyperhomocysteinemia [>100 μmol/l], .] Deficiencies in the remethylation reaction also result in a rise in Hcy.
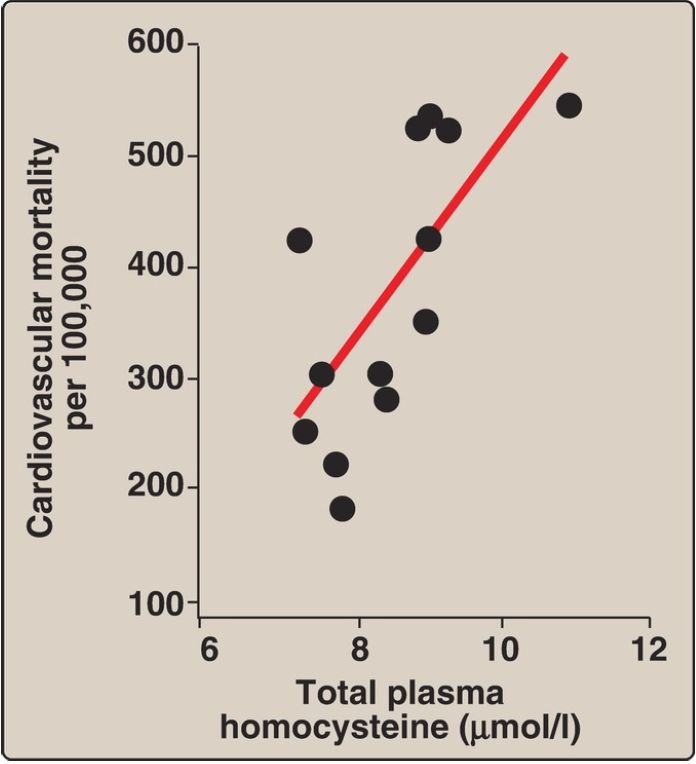
Figure 2: Association between cardiovascular disease mortality and total
plasma homocysteine.
Elevated homocysteine and decreased folic acid levels in pregnant women are associated with increased incidence of neural tube defects (improper closure, as in spina bifida) in the fetus. Periconceptual supplementation with folate reduces the risk of such defects.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


