
NADPH Role in White Blood Cell Phagocytosis and Microbe Killing
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 28-9-2021
28-9-2021
 1660
1660
NADPH Role in White Blood Cell Phagocytosis and Microbe Killing
Phagocytosis is the ingestion by receptor-mediated endocytosis of microorganisms, foreign particles, and cellular debris by WBC (leukocytes) such as neutrophils and macrophages (monocytes). It is an important defense mechanism, particularly in bacterial infections. Neutrophils and monocytes are armed with both oxygen-independent and oxygen-dependent mechanisms for killing bacteria.
1. Oxygen-independent Oxygen-independent mechanisms use pH changes in phagolysosomes and lysosomal enzymes to destroy pathogens.
2. Oxygen-dependent Oxygen-dependent mechanisms include the enzymes NADPH oxidase and myeloperoxidase (MPO) that work together in killing bacteria (Fig. 1). Overall, the MPO system is the most potent of the bactericidal mechanisms. An invading bacterium is recognized by the immune system and attacked by antibodies that bind it to a receptor on a phagocytic cell. After internalization of the microorganism has occurred, NADPH oxidase, located in the leukocyte cell membrane, is activated and reduces O2 from the surrounding tissue to superoxide (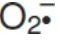 ), a free radical ROS, as NADPH is oxidized. The rapid consumption of O2 that accompanies formation of
), a free radical ROS, as NADPH is oxidized. The rapid consumption of O2 that accompanies formation of 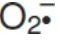 is referred to as the respiratory burst. [Note: Active NADPH oxidase is a membrane-associated complex containing a flavocytochrome plus additional peptides that translocate from the cytoplasm upon activation of the leukocyte. Electrons move from NADPH to O2 via flavin adenine nucleotide (FAD) and heme, generating
is referred to as the respiratory burst. [Note: Active NADPH oxidase is a membrane-associated complex containing a flavocytochrome plus additional peptides that translocate from the cytoplasm upon activation of the leukocyte. Electrons move from NADPH to O2 via flavin adenine nucleotide (FAD) and heme, generating 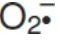 . Rare genetic deficiencies in NADPH oxidase cause chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) characterized by severe, persistent infections and the formation of granulomas (nodular areas of inflammation) that sequester the bacteria that were not destroyed.]
. Rare genetic deficiencies in NADPH oxidase cause chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) characterized by severe, persistent infections and the formation of granulomas (nodular areas of inflammation) that sequester the bacteria that were not destroyed.] 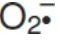 Next, is converted to H2O2 (also a ROS), either spontaneously or catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. In the presence of MPO, a hemecontaining lysosomal enzyme present within the phagolysosome, peroxide plus chloride ions are converted to hypochlorous acid ([HOCl] the major component of household bleach), which kills the bacteria. The peroxide can also be partially reduced to the hydroxyl radical (OH•), a ROS, or be fully reduced to H2O by catalase or glutathione peroxidase. [Note: Deficiencies in MPO do not confer increased susceptibility to infection because peroxide from NADPH oxidase is bactericidal.]
Next, is converted to H2O2 (also a ROS), either spontaneously or catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. In the presence of MPO, a hemecontaining lysosomal enzyme present within the phagolysosome, peroxide plus chloride ions are converted to hypochlorous acid ([HOCl] the major component of household bleach), which kills the bacteria. The peroxide can also be partially reduced to the hydroxyl radical (OH•), a ROS, or be fully reduced to H2O by catalase or glutathione peroxidase. [Note: Deficiencies in MPO do not confer increased susceptibility to infection because peroxide from NADPH oxidase is bactericidal.]

Figure 1: Phagocytosis and the oxygen (O2)-dependent pathway of microbial killing. IgG = immunoglobulin G; NADP(H) = nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; =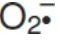 superoxide; H2O2 = hydrogen peroxide; HOCl =hypochlorous acid; OH• = hydroxyl radical.
superoxide; H2O2 = hydrogen peroxide; HOCl =hypochlorous acid; OH• = hydroxyl radical.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


