
NADPH Role in Hydrogen Peroxide Reduction
 المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
المؤلف:
Denise R. Ferrier
 المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 28-9-2021
28-9-2021
 1784
1784
NADPH Role in Hydrogen Peroxide Reduction
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is one of a family of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are formed from the partial reduction of molecular oxygen ([O2], Fig. 1A). These compounds are formed continuously as byproducts of aerobic metabolism, through reactions with drugs and environmental toxins, or when the level of antioxidants is diminished, all creating the condition of oxidative stress. These highly reactive oxygen intermediates can cause serious chemical damage to DNA, proteins, and unsaturated lipids and can lead to cell death. ROS have been implicated in a number of pathologic processes, including reperfusion injury, cancer, inflammatory disease, and aging. The cell has several protective mechanisms that minimize the toxic potential of these compounds. [Note: ROS can also be generated in the killing of microbes by white blood cells (WBC).]
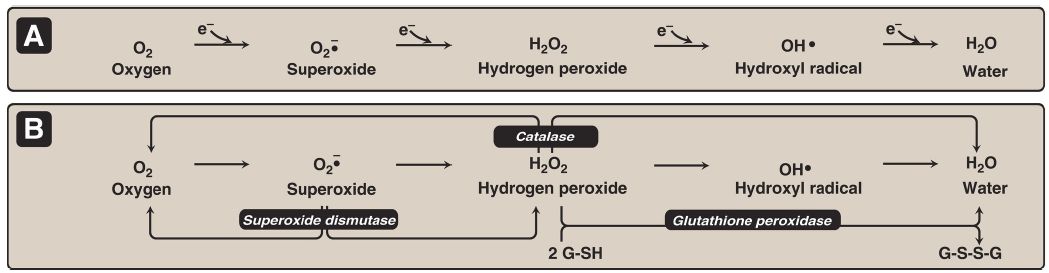
Figure 1: A. Formation of reactive intermediates from oxygen. e− = electrons.
B. Actions of antioxidant enzymes. G-SH = reduced glutathione; G-S-S-G =oxidized glutathione. [Note: See Fig. 13.6B for the regeneration of G-SH.] 1. Enzymes that catalyze antioxidant reactions Reduced glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide-thiol (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) present in most cells, can chemically detoxify H2O2 (Fig. 1B). This reaction, catalyzed by the selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase, forms oxidized glutathione (G-S-S-G), which no longer has protective properties. The cell regenerates G-SH in a reaction catalyzed by glutathione reductase, using NADPH as a source of reducing equivalents. Thus, NADPH indirectly provides electrons for the reduction of H2O2 (Fig. 2).
Additional enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, catalyze the conversion of other ROS to harmless products (see Fig.1B). As a group, these enzymes serve as a defense system to guard against the toxic effects of ROS.

Figure 2: A. Structure of reduced glutathione (G-SH). [Note: Glutamate is linked to cysteine through a γ-carboxyl, rather than an α-carboxyl.] B.The roles of G-SH and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) in the reduction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to water. G-S-S-G = oxidized glutathione.
2. Antioxidant chemicals A number of intracellular reducing agents, such as ascorbate , vitamin E , and β-carotene , are able to reduce and, thereby, detoxify ROS in the laboratory.
Consumption of foods rich in these antioxidant compounds has been correlated with a reduced risk for certain types of cancers as well as decreased frequency of certain other chronic health problems. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that the effects of these compounds are, in part, an expression of their ability to quench the toxic effect of ROS.
However, clinical trials with antioxidants as dietary supplements have failed to show clear beneficial effects. In the case of dietary supplementation with β-carotene, the rate of lung cancer in smokers increased rather than decreased. Thus, the health-promoting effects of dietary fruits and vegetables likely reflect a complex interaction among many naturally occurring compounds, which has not been duplicated by consumption of isolated antioxidant compounds.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الحيوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


