Mevalonate Pathway
Step 1 - Claisen Condensation
An early step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and other ‘isoprenoid’ compounds is a Claisen condensation between two acetyl CoA molecules. An initial trans-thioesterase process transfers the acetyl group of the first acetyl CoA to an enzymatic cysteine (Reaction 1). In the Claisen condensation phase of the reaction, the alpha-carbon of a second acetyl CoA is deprotonated, forming an enolate (Reaction 2).

The enolate carbon attacks the electrophilic thioester carbon, forming a tetrahedral intermediate (Reaction 3) which quickly collapses to expel the cysteine thiol (Reaction 4) and produce acetoacetyl CoA.
Step 2 - Aldol Condensation
Acetyl CoA then reacts with the acetoacetyl CoA in an aldol-like addition. Subsequent hydrolysis produces (3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA (HMG-CoA).
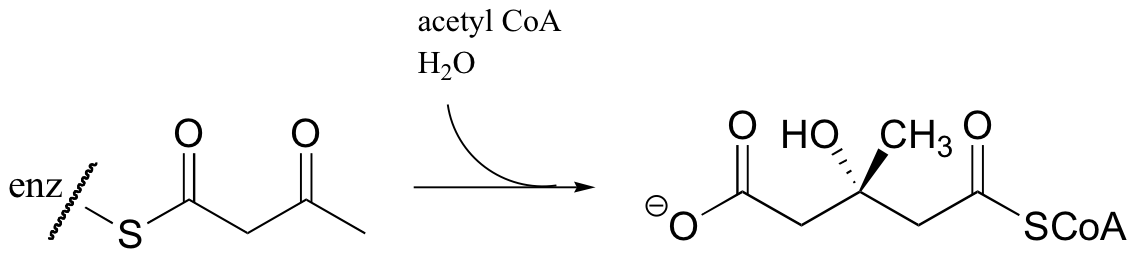
Generating HMG-CoA
Step 3 - Reduction of the Thioester
The thioester is reduced first to an aldehyde, then to a primary alcohol by two equivalents of NADPH producing (R)-mevalonate. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is the target of the statin family of cholesterol-lowering drugs.
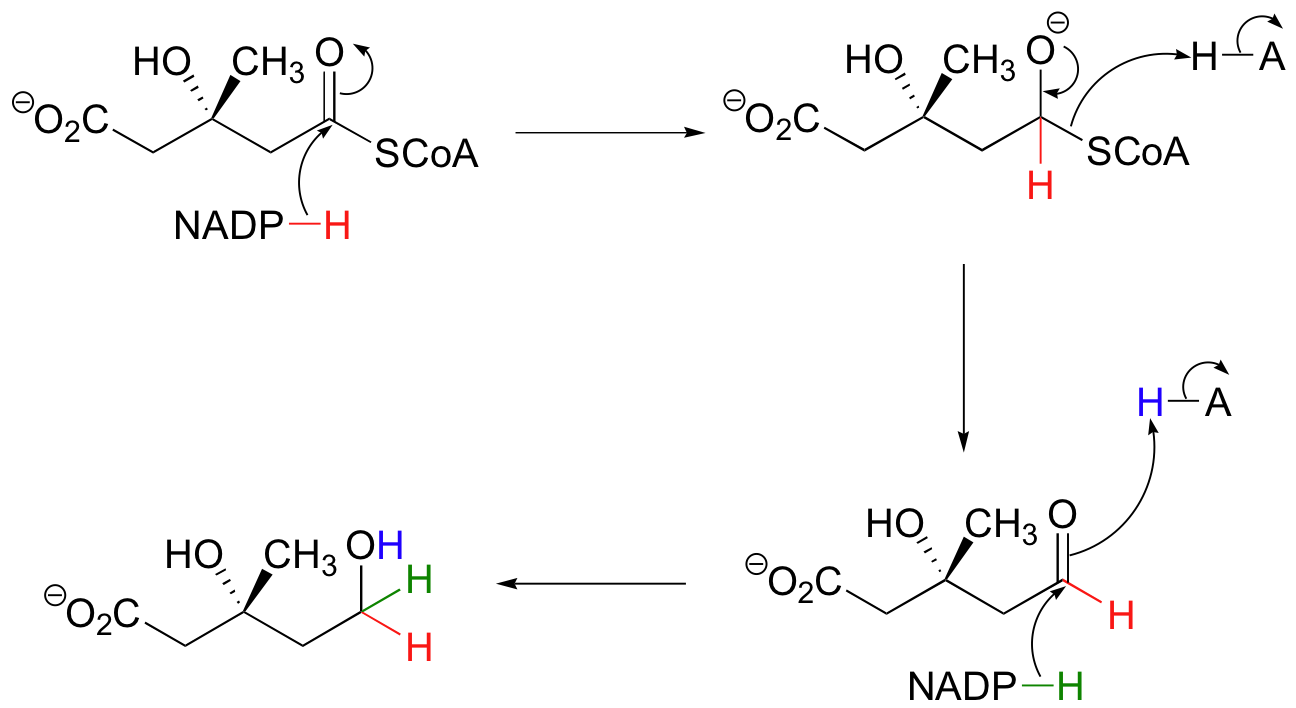
Generating (R)-Mevalonate
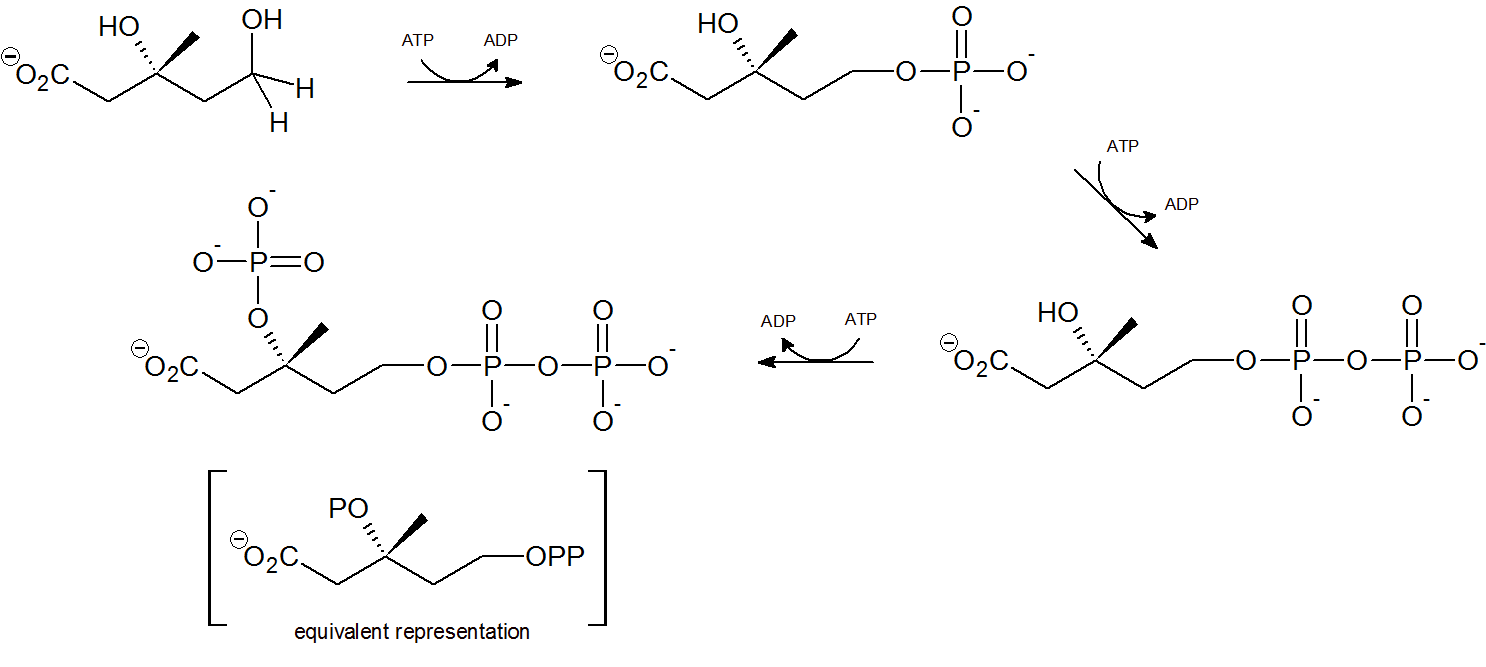
Step 4 - Mevalonate Phosphorylation
Two phsophorylations by adenosine triphosphate (ATP) occur at the terminal hydroxyl/phosphorus group through nucleophilic substitution, followed by a third ATP phosphorylation of the tertiary hydroxyl group.
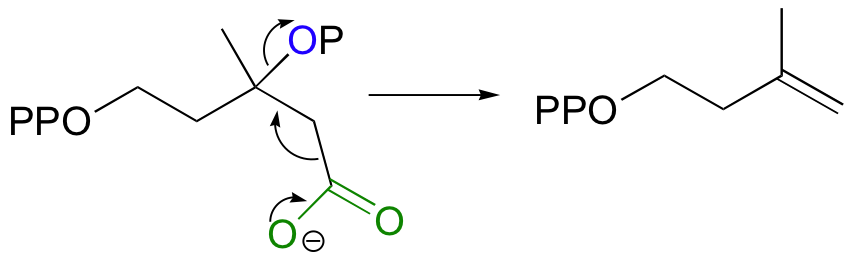
Step 5 - Decarboxylation
Finally isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP), the 'building block' for all isoprenoid compounds, is formed from a decarboxylation-elimination reaction.