
Lipid Soluble Vitamins
 المؤلف:
William Reusch
المؤلف:
William Reusch
 المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
............
الجزء والصفحة:
............
 17-8-2018
17-8-2018
 5362
5362
Lipid Soluble Vitamins
The essential dietary substances called vitamins are commonly classified as "water soluble" or "fat soluble". Water soluble vitamins, such as vitamin C, are rapidly eliminated from the body and their dietary levels need to be relatively high. The recommended daily allotment (RDA) of vitamin C is 100 mg, and amounts as large as 2 to 3 g are taken by many people without adverse effects. The lipid soluble vitamins, shown in the diagram below, are not as easily eliminated and may accumulate to toxic levels if consumed in large quantity. The RDA for these vitamins are:
Vitamin A 800 μg ( upper limit ca. 3000 μg)
Vitamin D 5 to 10 μg ( upper limit ca. 2000 μg)
Vitamin E 15 mg ( upper limit ca. 1 g)
Vitamin K 110 μg ( upper limit not specified)
From this data it is clear that vitamins A and D, while essential to good health in proper amounts, can be very toxic. Vitamin D, for example, is used as a rat poison, and in equal weight is more than 100 times as poisonous as sodium cyanide.
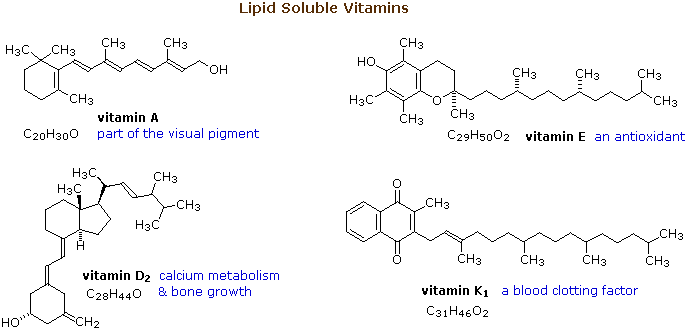
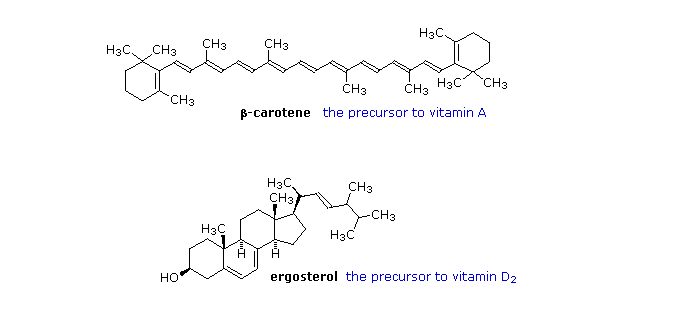
From the structures shown here, it should be clear that these compounds have more than a solubility connection with lipids. Vitamins A is a terpene, and vitamins E and K have long terpene chains attached to an aromatic moiety. The structure of vitamin D can be described as a steroid in which ring B is cut open and the remaining three rings remain unchanged. The precursors of vitamins A and D have been identified as the tetraterpene beta-carotene and the steroid ergosterol, respectively.
 الاكثر قراءة في الدهون
الاكثر قراءة في الدهون
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


