


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-8-2017
Date: 22-8-2017
Date: 31-8-2017
|
Catalytic Cracking
Catalytic cracking (Cat-cracking) is a remarkably versatile and flexible process. Its principal aim is to crack lower-value stocks and produce higher-value light and middle distillates. The process also produces light hydrocarbon gases, which are important feedstocks for petrochemicals. Catalytic cracking produces more gasoline of higher octane than thermal cracking. This is due to the effect of the catalyst, which promotes isomerization and dehydrocyclization reactions.
Products from catalytic cracking units are also more stable due to a lower olefin content in the liquid products. This reflects a higher hydrogen transfer activity, which leads to more saturated hydrocarbons than in thermally cracked products from delayed coking units, for example.
The feeds to catalytic cracking units vary from gas oils to crude residues. Heavier feeds contain higher concentrations of basic and polar molecules as well as asphaltenes. Examples are basic nitrogen compounds, which are readily adsorbed on the catalyst acid sites and lead to instantaneous albeit temporary deactivation. Polycyclic aromatics and asphaltenes contribute strongly to coke formation. FCC (fluid catalytic cracking) catalyst deactivation in resid processing have been reviewed by O’Connor et al. and Occelli. These feedstocks are often pretreated to decrease the metallic and asphaltene contents. Hydrotreatment, solvent extraction, and propane deasphalting are important treatment Excessive asphaltene and aromatics in the feed are precursors to carbon formation on the catalyst surface, which substantially reduces its activity and produces gasolines of lower quality.
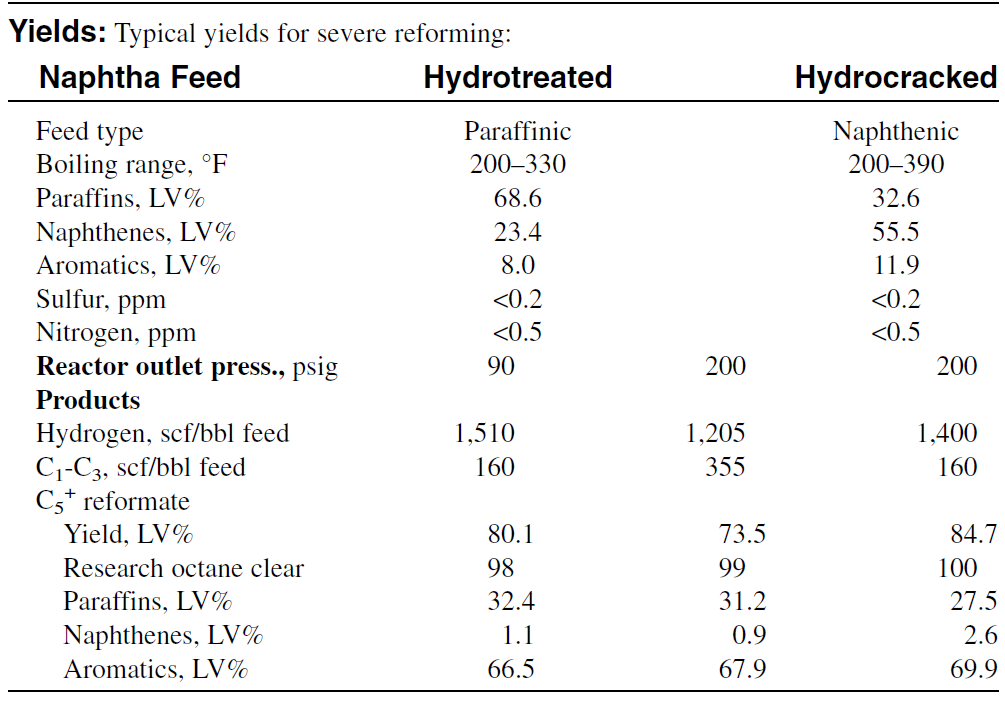
Residium fluid catalytic cracking (RFCC) has gained wide acceptance due to a larger production of gasoline with only small amounts of lowvalue products. Pretreating the feed in a low-severity residue desulfurization (RDS) increased the gasoline yield by 7.4%.19 Table 1-1 compares the effect of RDS pretreatment on product yields from RFCC (with and without RDS).
Table 1.1 : Properties of feed and products from Chevron Rheiniforming process



|
|
|
|
"عادة ليلية" قد تكون المفتاح للوقاية من الخرف
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ممتص الصدمات: طريقة عمله وأهميته وأبرز علامات تلفه
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
المجمع العلمي للقرآن الكريم يقيم جلسة حوارية لطلبة جامعة الكوفة
|
|
|