


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 4-3-2019
Date: 13-2-2019
Date: 19-1-2019
|
Systems of linear equations take place when there is more than one related math expression. For example, in y = 3x + 7, there is only one line with all the points on that line representing the solution set for the above equation.
When you face 2 equations in the SAME QUESTION, there will be two lines on the same xy-plane. The following two equations are graphed on the same xy-plane:
y = 3x + 5
y = - x
The solution set to any equation is the place where BOTH equations meet on the xy-plane. This meeting place is called the Point of Intersection. If you have a linear equation and a quadratic equation on the same xy-plane, there may be TWO POINTS where the graph of each equation will meet or intersect.
Here's a geometric view:
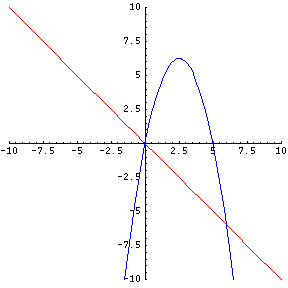
Here is a sample of two equations with two unknown variables.
Sample:
Solve
x + y = 10
3x + 2y = 20
There are three methods to solve our sample question:
1) We can solve it graphically
2) We can solve it algebraically
3) We can also solve it through algebraic elimination
I will solve the question using all 3 methods.
Method 1: Solve Graphically
To solve graphically, it is best to write BOTH equations in the slope-intercept form or in the form: y = mx + b where m = the slope and b = the y-intercept as your first step.
So, x + y = 10 becomes y = - x + 10 (slope-intercept form)
NEXT: 3x + 2y = 20 becomes y = -3x/2 + 10 (slope-intercept form)
Step 2: Plug different values for x to find points in the (x,y) form leading to the point of intersection.
After doing the algebra, I found that BOTH equations meet at point (0,10) . Point (0,10) means that if you plug x = 0 and y = 10 into BOTH original equations, you will find a balance of the equations. In other words, you will get the SAME ANSWER on BOTH sides of each original equation.
Here's what these two equations look like on the xy-plane:
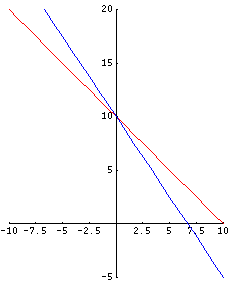
Method 2: Solve algebraically
Steps:
1) Solve for eaither x or y in the first equation (x + y = 10).
I will solve for y. So, x + y = 10 becomes y = -x + 10, which really means
" y in terms of x."
2) Plug the value of y (that is, -x + 10) in the second equation to find x.
Our second equation is: 3x + 2y = 20.
3x + 2(-x + 10 ) = 20
Next: Solve for x
3x -2x + 20 = 20
x + 20 = 20
x = 0.
3) Plug x = 0 into EITHER original equations to find the value of y.
I will use our second equation.
3x + 2y = 20
3(0) + 2y = 20
0 + 2y = 20
2y = 20
y = 10.
So, our point of intersection is once again (0,10).
Method 3: Algebraic Elimination
This method deals with matching the variables to ELIMINATE or do away with.
Keep in mind that it is your choice which variable you want to eliminate first.
GOAL: Eliminate x and solve for y or vice-versa. Let's go back to our original equations.
In our second 3x + 2y = 20, you can eliminate 3x by multiplying -3 by EVERY term in our first equation (x + y = 10).
x + y = 10
3x + 2y = 20
-3(x) + -3(y) = -3(10)
3x + 2y = 20
-3x + -3y = -30
3x + 2y = 20
NOTICE that -3x and 3x are eliminated. See it? See why? Here's why: A negative PLUS a positive = ZERO.
We now have this:
-3y = -30
2y = 20
-3y + 2y = -30 + 20
-y = -10
y = 10.
Next: To find x, we plug y = 10 into EITHER of the original equations. By now you should see that our answer for x will be ZERO.
Here it is:
I will use x + y = 10
x + 10 = 10
x = 0.



|
|
|
|
4 أسباب تجعلك تضيف الزنجبيل إلى طعامك.. تعرف عليها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
أكبر محطة للطاقة الكهرومائية في بريطانيا تستعد للانطلاق
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تبحث مع العتبة الحسينية المقدسة التنسيق المشترك لإقامة حفل تخرج طلبة الجامعات
|
|
|