


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-2-2018
Date: 29-6-2020
Date: 8-3-2019
|
Double displacement reactions
In single displacement reactions (see the preceding section), only one chemical species is displaced. In double displacement reactions, or metathesis reactions, two species (normally ions) are displaced. Most of the time, reactions of this type occur in a solution, and either an insoluble solid (in precipitation reactions) or water (in neutralization reactions) will be formed.
Precipitation reactions: Forming solids
The formation of an insoluble solid in a solution is called precipitation. For instance, if you mix a solution of potassium chloride and a solution of silver nitrate, a white insoluble solid forms in the resulting solution. Here are the molecular, ionic, and net-ionic equations for this double-displacement reaction:
Molecular: KCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
Ionic: K+ + Cl– + Ag+ + NO3– → AgCl(s) + K+ + NO3–
Net-ionic: Cl– + Ag+ → AgCl(s)
The white insoluble solid that forms (AgCl) is silver chloride. You can drop out the potassium cation and nitrate anion spectator ions, because they don’t change during the reaction and are found on both sides of the equation in an identical form. To write these equations, you have to know something about the solubility of ionic compounds:
✓ If a compound is soluble, it will not react at all and you can represent it by the appropriate ions or use (aq).
✓ If a compound is insoluble, it will precipitate (form a solid).
Table 1-1 Solubilities of Selected Ionic Compounds
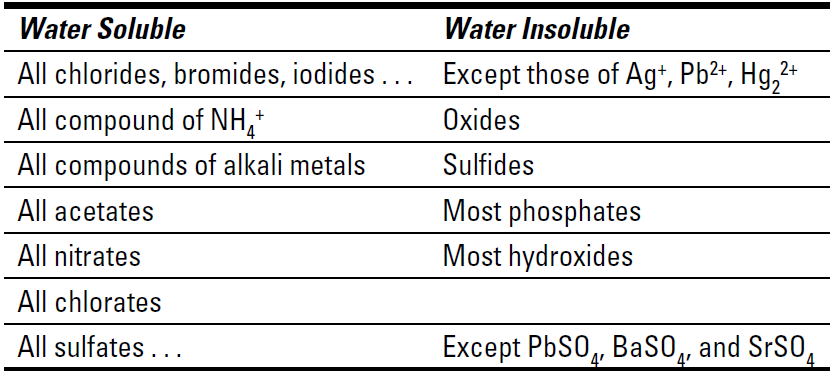
To use Table 1-1, take the cation of one reactant and combine it with the anion of the other reactant (and vice versa), keeping the neutrality of the compounds. This allows you to predict the possible products of the reaction. Then look up the solubilities of the possible products in the table. If the compound is insoluble, it’ll precipitate. If it’s soluble, it’ll remain in solution.
Neutralization reactions: Forming water
Besides precipitation the other type of double-displacement reaction is the reaction between an acid and a base. This double-displacement reaction, called a neutralization reaction, forms water.
Take a look at the mixing solutions of sulfuric acid (auto battery acid, H2SO4) and sodium hydroxide (lye, NaOH). Here are the molecular, ionic, and net-ionic equations for this reaction:
Molecular: H2SO4(aq) + 2 NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
Ionic: 2H+ + SO42– + 2Na+ + 2OH– → 2Na+ + SO42– + 2H2O(l)
Net-ionic: 2H+ + 2OH– → 2H2O(l) or H+ + OH– → H2O(l)
To go from the ionic equation to the net-ionic equation, you let the spectator ions (those that don’t really react and that appear in an unchanged form on both sides on the arrow) drop out. Then reduce the coefficients in front of the reactants and products down to the lowest common denominator.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|