


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 30-12-2020
Date: 18-5-2016
Date: 13-2-2017
|
The Absorption of Heat by Solids and Liquids
Heat Capacity
If you put a certain amount of energy or heat into a block of wood then the temperature will increase by a certain amount. If you do the same thing to a lump of steel (of the same mass) its temperature increase will be larger than for the wood. Heat capacity tells us how much the temperature of an object will increase for a given amount of energy or heat input. It is defined as

where C is the heat capacity, Q is the heat and ΔT is the temperature change, or

Example Which has the largest heat capacity; wood or steel ?
Solution For a given Q then ΔT will be larger for steel. From
C = Q
ΔT it means that C is small for steel and large for wood.
Specific Heat
If we put a certain amount of heat into a small block of steel compared to a large block then the small block will change its temperature the most. Thus we also need to include the mass of the block in determining temperature change. Thus we define specific heat (with a lower case c) as

or

In other words the specific heat is just the heat capacity per unit mass or

Molar Specific Heat
Instead of defining specific heat with the mass of the object, we could define it according to the total number of molecules in the object. But if we write down the total number of molecules we will be writing down huge numbers. Now we always use other words for huge numbers. Instead of saying ''one hundred tens" we say ''thousand", i.e.
thousand ≡ 1000
or instead of saying ''one thousand thousands" we say ''million", i.e.
million ≡ 1, 000, 000
Now even million, billion and trillion are too small for the number of molecules in an object. Thus define

(This number arose because in 12 grams of 12C there is 1 mole of atoms). Thus molar specific heat is defined as

where N is the number of moles of molecules in the substance.
Example How much heat is required to increase the temperature of 2 kg of water from 20oC to 30oC ?
Solution The specific heat of water is 1.00 cal g-1K-1. Thus the temperature should be in oK. Now ΔT = 30oC – 20oC = 20oC or
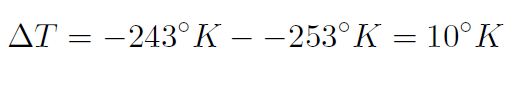
giving
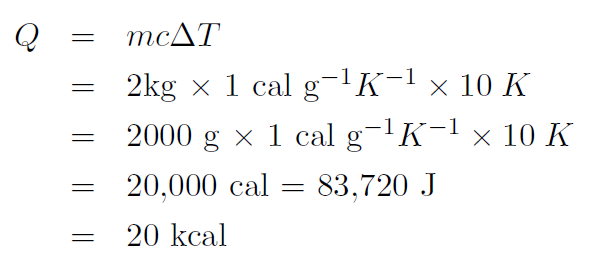
where we have used 1 cal ≡ 4.186 J.
Heats of Transformation
When you put heat or energy into an object the temperature does not always change! For example, if you put heat into a block of ice at 0oC it may just melt to a pool of water still at 0oC. Thus heat can cause a change of phase. Putting heat into water at 100oC may just vaporize the water to steam at 100oC. The heat of transformation L is defined via

where Q is the heat and m is the mass. If melting is involved L is called a heat of fusion Lf or for vaporizing L is called a heat of vaporization Lv.
Example How much heat is required to melt 2 kg of ice at 0oC to water at 0oC ?
Solution The latent heat of fusion is Lf = 79.5 cal g-1 giving




|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|