

 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 19-8-2016
Date: 7-8-2016
Date: 9-8-2016
|
Clausius–Clapeyron
a) Derive the Clausius–Clapeyron equation for the equilibrium of two phases of a substance. Consider a liquid or solid phase in equilibrium with its vapor.
b) Using part (a) and the ideal gas law for the vapor phase, show that the vapor pressure follows the equation ln PV = A – B/τ. Make reasonable assumptions as required. What is B?
SOLUTION
a) We know that, at equilibrium, the chemical potentials of two phases should be equal:
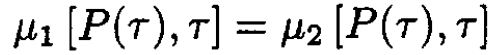 (1)
(1)
Here we write P ≡ P(τ) to emphasize the fact that the pressure depends on the temperature. By taking the derivative of (1) with respect to temperature, we obtain
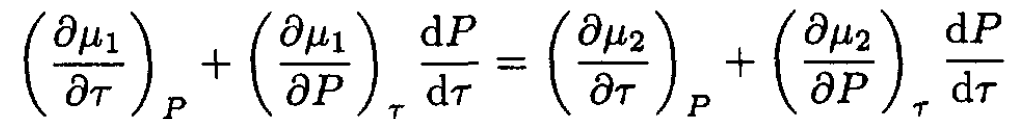 (2)
(2)
Taking into account that (∂μ/∂τ)p = -s and (∂μ/∂P)τ = v, where s and v are the entropy and volume per particle, and substituting into (2), we have
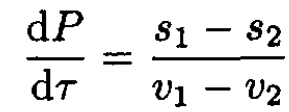 (3)
(3)
where subscripts 1 and 2 refer to the two phases. On the other hand, q = τ(s2 – s1), where q is the latent heat per particle, so we can rewrite (3) in the form
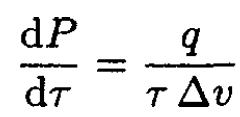 (4)
(4)
which is the Clausius–Clapeyron equation.
b) Consider the particular case of equilibrium between liquid and vapor. The volume v1 of the liquid is usually much smaller than that for the vapor v2, so we can disregard v1 in (4) and write
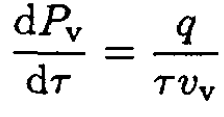 (5)
(5)
Using the ideal gas law for vapor, vv = τ/Pv, we get
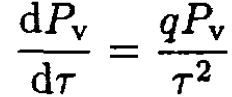 (5)
(5)
or
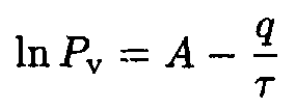 (6)
(6)
We can see that B = q. Rewriting (6) in usual units gives
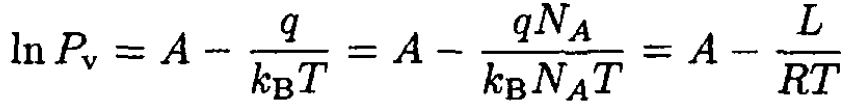
where L is the latent heat per mole, NA is Avogadro’s number, and R is the gas constant.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|